COVID-19: Agencies Increased Use of Some Regulatory Flexibilities and Are Taking Steps to Assess Them
Fast Facts
During the pandemic, federal agencies adapted their regulations to meet emergent needs. For example, agencies waived some eligibility requirements to expand access to food assistance programs.
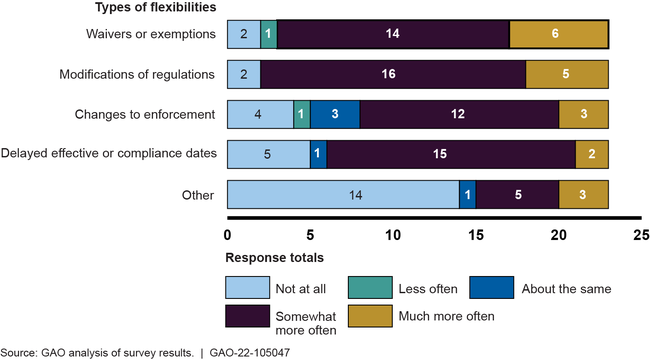
In our survey of 24 major agencies, most reported using these regulatory flexibilities more often than usual.
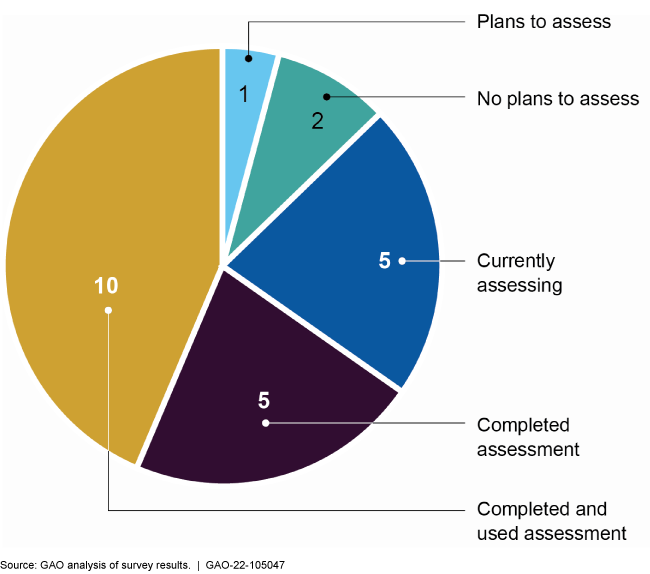
Assessing flexibilities can help agencies understand successes or challenges. 15 agencies in our survey said they had finished assessing at least one of the flexibilities they used.
Agencies that hadn't finished assessments said it was because
- The flexibilities are temporary
- The agencies are still focused on pandemic response
Agencies reported progress in assessing pandemic-related regulatory flexibilities
Highlights
What GAO Found
Twenty-three of 24 major agencies GAO surveyed reported implementing regulatory flexibilities in response to COVID-19. Regulatory flexibilities can include actions that modify regulatory standards, as well as activities that modify their applicability (e.g., through waivers or exemptions) or enforcement. A majority of agencies reported increased use of multiple types of flexibilities in response to COVID-19 compared to before the pandemic (see figure).
Agencies' Change in Use of Regulatory Flexibilities in Response to the COVID-19 Pandemic
Officials from each of the five agencies GAO interviewed—the Departments of Energy, Homeland Security, and Transportation, as well as the Environmental Protection Agency and the Small Business Administration—reported designing and implementing flexibilities based on internal expertise developed from prior events. For example, officials reported that their experiences managing Ebola, constrained funding situations, and natural disasters—such as Hurricanes Sandy and Maria—helped them develop responses to COVID-19. Officials from these agencies stated that they generally did not rely on specific plans, policies, or other tools given the unique challenges posed by COVID-19.
Fifteen of the 24 agencies GAO surveyed reported having already completed an assessment of at least one regulatory flexibility to understand successes or challenges with using them. Ten agencies reported having used at least one such assessment to inform their decision-making, such as whether to modify an existing flexibility or use a new flexibility. Officials from several of the selected agencies reported that their agencies had not conducted assessments of at least one of the flexibilities discussed with GAO. Among reasons why assessments were not conducted, officials said that some flexibilities were intended to be temporary, and that their focus remained on responding to and recovering from the ongoing pandemic.
Why GAO Did This Study
Federal regulations can generate substantial benefits to society, but benefits can diminish if regulations are not adapted to meet emerging public needs. Federal agencies have implemented regulatory flexibilities to address the COVID-19 pandemic's substantial effect. Regulatory flexibilities are actions taken, at least in part, to temporarily reduce regulatory burdens or constraints imposed on regulated entities.
The CARES Act includes a provision for GAO to report on its COVID-19 pandemic oversight efforts. GAO was also asked to look at regulatory flexibilities available to agencies in responding to COVID-19. For this report, GAO examines (1) agencies' implementation of regulatory flexibilities in response to the pandemic; (2) the plans, policies, and other tools selected agencies used to identify and design regulatory flexibilities; and (3) efforts these selected agencies took to assess the impacts of regulatory flexibilities.
To do so, in October 2021, GAO surveyed 24 major federal agencies—those identified in the Chief Financial Officers Act of 1990, as amended—regarding their use of COVID-19 regulatory flexibilities. GAO also interviewed officials at five agencies in part because those agencies reported using more types of flexibilities in response to COVID-19 compared to before the pandemic. GAO interviewed officials about how they identified, designed, and assessed their flexibilities. GAO also reviewed GAO's work related to major agencies' COVID-19 flexibilities, and summarized examples of these flexibilities, as appropriate.
For more information, contact Yvonne D. Jones at (202) 512-6806 or JonesY@gao.gov.
