Veterans Affairs: Use of Additional Funding for COVID-19 Relief
Fast Facts
As of April 14, 2021, the Department of Veterans Affairs reported 224,538 cumulative COVID-19 cases among veterans, with 11,366 deaths.
The VA received $19.6 billion in supplemental funding in March 2020 to respond to the pandemic.
Our analysis shows that through March 2021, VA had committed to spending $9.9 billion and spent $8.1 billion of this funding. Much of the committed funding went to veterans' health care from non-VA providers, additional salary costs (such as for overtime), and to help homeless veterans.
The VA plans to use its remaining funding on testing, equipment, distributing vaccines, and more.
Breakdown of the VA health care system’s use of the majority of the supplemental funding through Feb. 2021 (in millions)
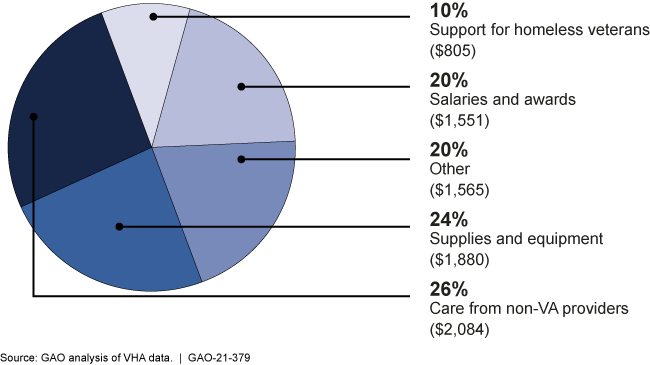
Highlights
What GAO Found
The Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) received $19.6 billion in supplemental funding—additional funding above the annual appropriation—in March 2020 to respond to the COVID-19 pandemic. GAO's analysis of VA data shows that through March 2021, VA had obligated $9.9 billion and expended $8.1 billion of the supplemental funding.
Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Reported Obligations and Expenditures of CARES Act and Families First Coronavirus Response Act Funding through March 2021
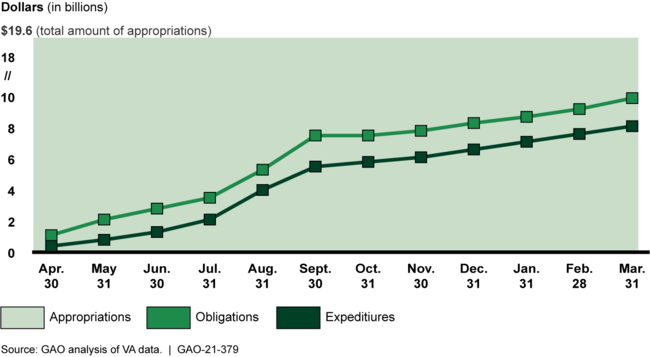
Note: An obligation is a definite commitment that creates a legal liability to pay, and an expenditure is the actual spending of money.
The majority of the obligated supplemental funding ($8.3 billion) was obligated by VA's Veterans Health Administration (VHA) for care provided to veterans by non-VA providers, the additional costs of salaries (such as for overtime) and related expenses of VHA staff, supplies and materials, and support for homeless veterans, due to COVID-19 response. The remaining obligations included costs of VA's transition to telehealth and telework during the COVID-19 pandemic, primarily through the Office of Information Technology (OIT). According to spend plan documents and department officials, VA plans to obligate its remaining $9.7 billion in funding on activities including COVID-19 testing, purchasing supplies and equipment, and distributing COVID-19 vaccines.
VA mainly relies on its standard financial management processes to oversee the use of supplemental funds, including establishing new versions of standard financial codes to account for and report on use of funds through VA's financial system. VA also collected details about the use of supplemental funding, such as descriptions of the activities for which funds were obligated, that were not available in its financial system. In addition, the VA components that received the majority of the supplemental funding—VHA and OIT—set up additional processes and issued guidance specific to the use of supplemental funding, such as establishing councils to review funding requests.
Why GAO Did This Study
As of April 14, 2021, VA reported 224,538 cumulative veteran cases of COVID-19, and 11,366 deaths. The CARES Act and Families First Coronavirus Response Act included supplemental funding for COVID-19 relief, and the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2021, permitted VA additional flexibility to transfer these funds across the department.
The CARES Act also included a provision for GAO to report on its ongoing monitoring and oversight efforts related to the COVID-19 pandemic.
This report examines 1) VA's obligations and expenditures of COVID-19 supplemental funding, as well as its plans to obligate remaining funds, and 2) how VA oversees the use of COVID-19 supplemental funds.
GAO reviewed VA data on obligations, expenditures, and spend plans for COVID-19 supplemental funding, as well as contracting documentation and documentation on the processes and guidance VA developed to oversee the use of funds. GAO interviewed VA officials responsible for oversight of the supplemental funding, including officials from five regional networks, selected based on funding levels and geography, to gather information about their roles in overseeing the use of and accounting for supplemental funding.
VA reviewed a draft of this report and provided a technical comment, which was incorporated as appropriate.
For more information, contact Sharon M. Silas at (202) 512-7114 or silass@gao.gov.
