Space Operations: DOD Is Pursuing Efforts to Collaborate with Allies and Partners but Needs to Address Key Challenges
Fast Facts
The Department of Defense's space operations and other activities, including exercises, are aimed at deterring and preparing for potential conflict. DOD emphasizes that collaborating with the nation's allies and other partners is critical to achieving its goals.
DOD collaborates closely with allies and partners but has trouble carrying out the work. For example, the U.S. Space Force doesn't have enough people in some units to plan and execute activities with allies and partners. Also, some DOD organizations have overlapping responsibilities for this work, which has caused confusion.
Our recommendations to DOD address these challenges and more.

Highlights
What GAO Found
The Department of Defense (DOD) uses various mechanisms and agreements to collaborate with allies and partners on space operations and other activities.
GAO found that DOD is increasing its efforts to integrate allies and partners into space operations and activities by establishing goals, but it faces persistent challenges that impede greater collaboration. DOD has acknowledged these challenges, but has not set specific milestones for implementing goals to integrate allies and partners into space operations. Establishing such milestones—and implementing them—is important given DOD’s strategic priority of working with allies and partners on space operations.
U.S. Space Operations and Activities with Select Allies and Partners
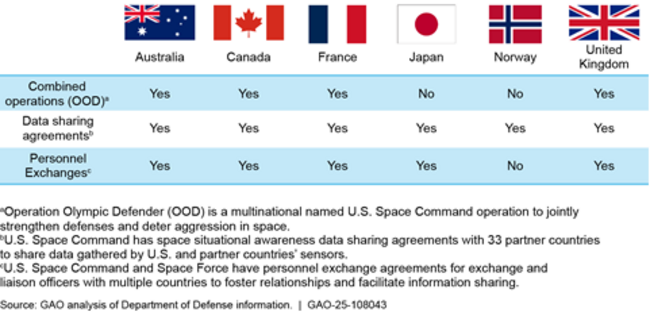
Further, DOD has several organizations that have overlapping roles and responsibilities for space-related security cooperation. This has resulted in ally and partner confusion and missed opportunities for coordination. For example, several foreign government officials said that finding the appropriate DOD contact with whom to coordinate is difficult. DOD has not issued guidance clarifying roles and responsibilities to inform these interactions internally and with allies and partners.Without such guidance, DOD organizations may continue to pursue space-related security cooperation activities outside established channels, leading to confusion and inefficiencies.
Lastly, GAO found that Space Force has not identified, analyzed, or responded to the risk of not filling positions within its service components, including space-related planning, information sharing, and security cooperation positions. Without doing this, Space Force risks undermining its goal of increasing collaboration with allies and partners.
This is a public version of a classified report that GAO issued in March 2025. Information that DOD deemed classified has been omitted.
Why GAO Did This Study
DOD recognizes that space capabilities are fundamental to all military operations. DOD also must cooperate with allies and partners on space operations if it is to deter and, if necessary, prevail in a high-end conflict.
Senate Report 118-58 accompanying a bill for the National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2024 included a provision for GAO to review DOD’s efforts to integrate allies and partners into space operations and activities. This report assesses, among other things, the extent to which DOD has integrated allies and partners into space operations and activities, defined roles and responsibilities for space-related security cooperation, and assessed personnel needs for engaging in space-related security cooperation.
To conduct this review, GAO reviewed space-related DOD guidance documents, and interviewed DOD and U.S. embassy officials. GAO also interviewed foreign government officials from six partner nations.
Recommendations
GAO is making three recommendations, including that DOD set milestones for implementing its goals for integrating allies and partners into space operations, identify, analyze, and respond to risks of understaffing positions within Space Force service components, and issue guidance for space-related security cooperation roles and responsibilities. DOD concurred with two recommendations and did not concur with the third. GAO continues to believe that all of the recommendations should be implemented, as discussed in the report.
Recommendations for Executive Action
| Agency Affected | Recommendation | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Department of Defense | The Secretary of Defense should ensure that the Assistant Secretary of Defense (Space Policy), in coordination with key stakeholders, sets specific milestones for implementing DOD's goals for integrating allies and partners into space operations as outlined in the International Space Cooperation Strategy. (Recommendation 1) |
When we confirm what actions the agency has taken in response to this recommendation, we will provide updated information.
|
| Department of the Air Force | The Secretary of the Air Force should ensure that the Chief of Space Operations programs for appropriate personnel levels within the Space Force components to combatant commands—including positions responsible for security cooperation, planning, and foreign disclosure—to optimize readiness and sustainability or identify, analyze, and respond to the risks of understaffing identified positions within its components to the combatant commands. (Recommendation 2) |
When we confirm what actions the agency has taken in response to this recommendation, we will provide updated information.
|
| Department of Defense | The Secretary of Defense should ensure that the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff issues guidance clarifying the space-related security cooperation roles and responsibilities for the relevant organizations throughout DOD—including Assistant Secretary of Defense (Space Policy), U.S. Space Command, and Space Force. (Recommendation 3) |
When we confirm what actions the agency has taken in response to this recommendation, we will provide updated information.
|
