Export-Import Bank: Additional Documentation about Stakeholder Roles and Clarity about Fraud Risks Would Strengthen Antifraud Efforts
Fast Facts
The Export-Import Bank of the United States supports American jobs by facilitating U.S. exports. It offers loans, loan guarantees, and other help to U.S. companies that cannot obtain private financing for their deals. It may assume risks that the private sector won't, including risk of losses due to fraud.
The bank has adopted antifraud practices as required by law.
We reviewed its 2020-2021 transactions to see if it denied applications from parties with fraud or corruption charges. We found no convicted parties among applicants.
Our recommendations address ways the bank could improve its responses to evolving risks of fraud and more.

Highlights
What GAO Found
The Export-Import Bank of the United States (EXIM) has designed and implemented an antifraud strategy and collaborated with stakeholders to ensure its implementation, but the strategy is missing key elements. EXIM's strategy includes specific control activities to prevent and detect fraud in accordance with leading practices, which reflect the types and impacts of fraud (see figure).
Types and Impacts of Potential Fraud at Export-Import Bank of the United States
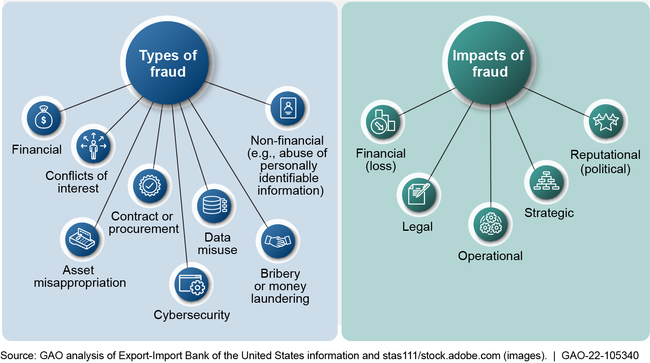
Further, EXIM identified risks that remained even after being mitigated by existing control activities that exceed its risk appetite. For those residual risks, EXIM identified and documented how the agency will respond to them, which better positions EXIM to prevent fraud risks that exceed its appetite. However, EXIM did not link these residual risks to its antifraud strategy. As described in fraud risk management leading practices, doing so helps program managers focus their activities. Without these linkages, EXIM cannot be assured that it is adequately addressing risks in a dynamic risk environment or that its approach addresses the fraud risks it identified and prioritized. EXIM also works with outside stakeholders, such as lenders and export credit insurance partners, to process transactions that that carry EXIM's guarantees. However, EXIM did not document these external stakeholders' roles and responsibilities for fraud controls in the strategy to ensure that all parties, including outside lenders and export credit insurance partners, understand their fraud-related responsibilities.
EXIM has established responsibilities and designed and implemented control activities to address its antifraud requirement, as required by its reauthorizing legislation. GAO also reviewed EXIM 2020-2021 transaction data to determine if EXIM had appropriately denied applications by parties convicted of EXIM-related fraud or corruption charges. GAO's analysis did not identify any relevant convicted parties within the EXIM transaction data.
Why GAO Did This Study
EXIM's mission is to support American jobs by facilitating the export of U.S. goods and services. Taxpayers could be responsible for losses arising from EXIM's operations, including losses due to fraud. The 2019 legislation reauthorizing EXIM included an antifraud requirement. Specifically, the legislation stated that EXIM shall deny an application for assistance if an individual has been convicted of an act of fraud or corruption in connection with an application for support from EXIM in the prior 5 years.
Since 2015, GAO has been mandated by law to periodically review EXIM's antifraud controls. This report assesses the extent to which EXIM has (1) designed and implemented an antifraud strategy and collaborated with stakeholders to ensure its implementation; and (2) established responsibilities and designed and implemented control activities to address its antifraud requirement as required by legislation. GAO assessed EXIM's activities against leading practices, reviewed EXIM documentation, and interviewed EXIM managers. GAO also reviewed EXIM transactions from January 1, 2020, to December 31, 2021—the most recent data available when GAO began its work.
Recommendations
GAO is making two recommendations to EXIM to (1) demonstrate links to its highest residual fraud risks within its antifraud strategy, and (2) document the roles and responsibilities of the external partners responsible for fraud controls. EXIM agreed with GAO's recommendations.
Recommendations for Executive Action
| Agency Affected | Recommendation | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Export-Import Bank of the United States | EXIM's Chair and President should update its antifraud strategy to demonstrate links to its highest internal and external residual fraud risks outlined in its fraud risk profile to its antifraud strategy. (Recommendation 1) |
In November 2022, EXIM provided GAO with a revised antifraud strategy indicating how residual fraud risks, identified as a result of the fraud risk assessment, will guide EXIM's fraud risk management efforts. For example, EXIM updated its strategy to describe how fraud awareness training will be provided to EXIM staff and management to make them aware of the highest fraud risks that have been identified through the biennial fraud risk assessment. By doing this, EXIM can better ensure that it is adequately addressing risks in a dynamic risk environment and that the program's approach appropriately addresses the prioritized fraud risks identified in the fraud risk assessment.
|
| Export-Import Bank of the United States | EXIM's Chair and President should update its antifraud strategy to document the roles and responsibilities of the external parties, specifically delegated authority lending (DAL) and Export Credit Insurance (ECI) partners, responsible for fraud controls. (Recommendation 2) |
In November 2022, EXIM provided GAO with a revised antifraud strategy outlining the roles and responsibilities of the external parties, specifically DAL and ECI parties, responsible for fraud controls. For example, EXIM documented within its strategy the DAL and ECI partners' fraud risk management and due diligence responsibilities when reviewing the participant and the transaction. By doing this, EXIM can better ensure that the roles and responsibilities related to fraud risk management are clearly understood by all parties involved in fraud risk management.
|
