Rail Transit: Federal Transit Administration Could Improve Information on Estimating Project Costs
Fast Facts
Rail transit projects are inherently complicated, take years to plan and construct, and can cost hundreds of millions to billions of dollars.
We looked at the factors affecting the cost of these projects. As part of our work, we selected 4 rail transit projects as case studies and interviewed the people involved in them from industry and government. We identified approaches that can help project sponsors—usually state and local government agencies—manage costs, including improving their cost estimation.
We recommended ways the Federal Transit Administration can help project sponsors increase the reliability of their cost estimates.
The Utah Transit Authority’s 10.6-mile Mid-Jordan Light Rail Project

A train pulls into a station
Highlights
What GAO Found
Rail transit construction project sponsors, typically state or local government entities, have a vested interest in controlling costs. Stakeholders GAO interviewed identified a variety of factors that affect a rail transit construction project's costs (see figure).
Types of Factors That Affect Rail Transit Project Construction Costs
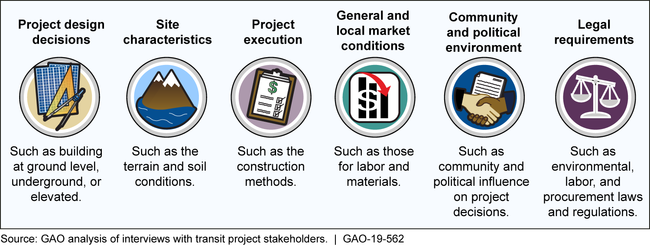
Project sponsors and other stakeholders identified various approaches sponsors have used to manage a project's costs. These approaches align with key project management principles GAO identified: (1) ensuring management capability; (2) making informed procurement decisions; (3) managing risk; and (4) managing stakeholder relationships. For example, sponsor officials and a contractor's representative from one GAO case study said they managed risk by cooperating to purchase steel materials early in the project to reduce the risk of additional steel price increases.
The Federal Transit Administration's (FTA) cost estimating information for sponsors aligns with many best practices, but FTA could improve the information's usefulness. GAO found that taken together, FTA's cost estimating information substantially or fully met 7 of the 12 cost estimating steps outlined in GAO's Cost Estimating and Assessment Guide (Cost Guide) but did not align with 5 of the steps. For example, the documents did not discuss sensitivity analyses—an assessment of each factor's effect on cost. Doing so could help sponsors better identify which cost factors are most likely to influence a project's overall costs if assumptions change, thereby improving an estimate's reliability and better informing sponsors' decisions. In addition, sponsors may have difficulty identifying critical cost estimating information because it is distributed across 14 different documents available to sponsors, 11 of which are intended for FTA's oversight contractors. By improving the content and organization of cost estimating information, FTA would help project sponsors increase the reliability of their cost estimates and reduce the risk of cost overruns.
Why GAO Did This Study
Rail transit projects are complex, and challenge sponsors to maximize limited resources. To help project sponsors build new or extend existing transit projects, Congress appropriated about $2.65 billion for FTA's 2019 Capital Investment Grants program.
Congress included a provision in a committee report for GAO to evaluate factors affecting the costs to build transit projects. This report examines: (1) stakeholders' views on factors that affect rail transit project costs, (2) stakeholders' views on approaches sponsors have used to manage costs, and (3) the extent to which FTA's cost estimating information for sponsors aligns with best practices in GAO's Cost Guide . GAO interviewed academic, construction, and other stakeholders identified through a literature search and referrals. GAO conducted case studies of four U.S. rail transit projects that received FTA grants and that were selected to obtain variation in transit mode, location, and other characteristics, and compared their approaches to GAO-identified key project management principles. GAO also interviewed FTA officials and compared FTA's cost estimating information with GAO's best practices.
Recommendations
FTA should (1) ensure that FTA's cost estimating information is consistent with all 12 steps in GAO's Cost Guide for developing reliable cost estimates and (2) provide a central, accessible source of cost estimating information for project sponsors. FTA partially concurred with the first and concurred with the second recommendation. GAO believes FTA should fully implement both recommendations.
Recommendations for Executive Action
| Agency Affected | Recommendation | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Federal Transit Administration | The FTA administrator should ensure that FTA's cost estimating information for project sponsors is consistent with all 12 steps found in GAO's Cost Estimating and Assessment Guide and needed for developing reliable cost estimates. [Recommendation 1] |
In January 2025, FTA published revised guidelines for the development of major transit capital projects to align with all 12 steps of GAO's Cost Guide. Specifically, FTA's revised Project and Construction Management Guidelines (Guidelines) now recommend that project sponsors consider applying the GAO 12-step methodology when developing a project cost estimate, including that project sponsors conduct a sensitivity analysis that identifies a range of possible costs based on varying major assumptions and parameters. The revised Guidelines describe each of the 12-steps in GAO's cost estimating methodology and directs the reader to GAO Cost Guide for further detail. As a result of this action, FTA has increased confidence that sponsors' cost estimates are based on sound procedures and are reliable.
|
| Federal Transit Administration | The FTA Administrator should provide a central, easily accessible source with all of FTA's cost estimating information to help project sponsors improve the reliability of their cost estimates. [Recommendation 2] |
Rail transit projects are inherently complicated, take years to plan and construct, and can cost hundreds of millions to billions of dollars. Consequently, these projects are often the subject of interest and scrutiny from the media, stakeholders, and the public, especially if the project encounters sizeable schedule delays and cost increases. We have previously reported that reliable cost estimates are critical to the success of any construction project, but federal agencies and their grantees have experienced challenges in estimating costs, with some projects costing more than expected and delivering results that do not satisfy all requirements. DOT provides grants and loans to help project sponsors-typically state or local government entities-build new transit systems or extend existing service, such as through the Federal Transit Administration's Fixed Guideway Capital Investment Grants (CIG) program. Through the CIG program, project sponsors or their contractors develop and revise cost estimates throughout project development, engineering, and construction to inform key decisions, such as determining how much funding to request from FTA. In 2019, we found that although FTA's cost estimating information for project sponsors aligns with many best practices, FTA does not provide sponsors with a centralized, authoritative source of this information that integrates cost estimating best practices. Specifically, we found that project sponsors may have difficulty identifying critical cost estimating information because it is distributed across 14 different documents available to sponsors, 11 of which are intended for FTA's oversight contractors. According to federal standards of internal control, FTA should communicate quality information externally so that external parties, such as project sponsors, can help achieve the project's objectives. We found that without a centralized, authoritative source of cost estimating information that clearly indicates that project sponsors are the intended audience, there is potential for a sponsor to overlook vital information. Therefore, we recommended that FTA should provide a central, easily accessible source with all of FTA's cost estimating information to help project sponsors improve the reliability of their cost estimates. In 2021, FTA created a new webpage that consolidates information on cost estimation for FTA funded transit projects for project sponsors. For example, the new webpage states that establishing a reliable baseline cost estimate is a critical element for successful projects, and it integrates cost estimating best practices by pointing project sponsors to the 12-step methodology found in GAO's Cost Estimating and Assessment Guide. In addition, the webpage provides information on: (1) FTA's cost estimation requirements, (2) how FTA evaluates cost estimates, (3) documents that project sponsors are to submit to FTA, and (4) FTA resources for estimating project costs, including information on historical data for transit capital projects. As a result of these actions, project sponsors have a centralized, easily accessible, and authoritative source of cost estimating information from FTA to help project sponsors increase the reliability of their cost estimates and reduce the risk of cost overruns.
|
