U.S. Secret Service: Further Actions Needed to Fully Address Protective Mission Panel Recommendations
Fast Facts
After an intruder ran past Secret Service personnel and entered the White House in 2014, an independent review panel found that this incident arose from a “catastrophic failure of training" in the Secret Service.
We found that the Secret Service implemented 11 of this panel's recommendations, but has yet to fully address the remaining 8. For example, the panel recommended that certain Secret Service agents train for 25% of their work time. However, these agents trained for 6% or less of their work hours in FY 2018.
We recommended that the Secret Service develop and implement a plan to reach its annual training targets.
Share of Regular Work Hours of Certain Special Agents Spent in Training, FYs 2014-2018
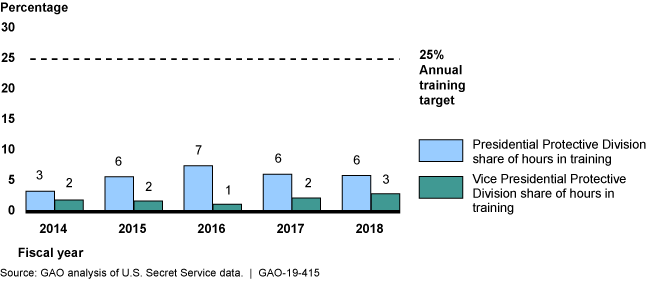
A bar graph showing that these divisions generally spent around 6% and 3% of their time in training, respectively.
Highlights
What GAO Found
The U.S. Secret Service (Secret Service) has made progress implementing the 19 recommendations related to training and personnel; technology, perimeter security, and operations; and leadership made by the U.S. Secret Service Protective Mission Panel (Panel). The Secret Service fully implemented 11 of the recommendations. For example, the agency increased the number of agents and officers in the divisions that protect the President and White House and secured approval to build a new fence around the White House complex.
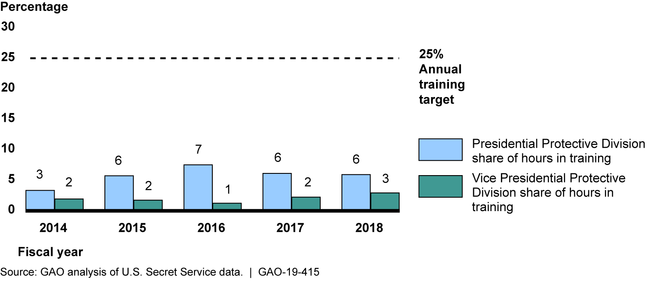
The Secret Service is in the process of implementing the remaining eight recommendations. The Panel found that the security incident of September 19, 2014, when an intruder jumped the north fence and entered the White House, arose from a “catastrophic failure of training.” The Panel recommended, and the Secret Service agreed, that the Presidential and Vice Presidential Protective Divisions train for 25 percent of their work time. However, the Secret Service has not met this target and lacks a plan for achieving it. In fiscal year 2018, special agents assigned to these divisions trained for about 6 percent and 3 percent, respectively, of their regular work hours (see figure). In commenting on a draft of this report in May 2019, the Secret Service stated that it no longer agrees with the training target and plans to reevaluate it. Developing and implementing a plan for ensuring that the established training target is met given current and planned staffing levels would better ensure that agents assigned to the Presidential and Vice Presidential Protective Divisions are prepared to carry out Secret Service's protection priority.
Share of Regular Work Hours Special Agents Assigned to the Presidential and Vice Presidential Protective Divisions Spent in Training, Fiscal Years 2014–2018
In addition, the Secret Service does not have a policy with a documented process for collecting complete and appropriate (i.e., protection-related) training hour data for Uniformed Division officers. Implementing such a policy will better position the Secret Service to assess the training data and make informed decisions about whether and how training needs are being met.
Why GAO Did This Study
The Secret Service, a component of the Department of Homeland Security (DHS), is responsible for protecting the President, the Vice President, and their families, as well as the White House complex. In October 2014, following several security lapses, the Secretary of Homeland Security established the Panel, an independent panel of experts, to review White House security and other aspects of Secret Service operations.
The Secret Service Recruitment and Retention Act of 2018 contains a provision for GAO to report on the progress made by the Secret Service in implementing the Panel's recommendations. This report addresses the extent to which the Secret Service has implemented the recommendations in the Panel's 2014 report. GAO reviewed Secret Service documents, analyzed agency training and labor-distribution data from fiscal years 2014 through 2018, and interviewed agency officials and Panel members.
Recommendations
GAO is making recommendations to the Secret Service: (1) develop and implement a plan to ensure that special agents assigned to the Presidential and Vice Presidential Protective Divisions reach annual training targets, and (2) develop and implement a policy that documents the process for collecting complete and appropriate data on Uniformed Division officer training. DHS concurred with the two recommendations.
Recommendations for Executive Action
| Agency Affected | Recommendation | Status |
|---|---|---|
| United States Secret Service |
Priority Rec.
The Director of the Secret Service should develop and implement a plan to ensure that special agents assigned to Presidential Protective Division and Vice Presidential Protective Division reach annual training targets given current and planned staffing levels. (Recommendation 1) |
In May 2019, we reported that the Secret Service had not met the established training target (25 percent of work time) and lacked a plan for achieving it. The U.S. Secret Service Protective Mission Panel (Panel) recommended that the Presidential and Vice Presidential Protective Divisions train for 25 percent of their work time. We found that, in fiscal year 2018, PPD and VPD special agents reported attending training for 5.9 percent and 2.9 percent of their regular work hours, respectively. We therefore recommended that the Director of the Secret Service develop and implement a plan to ensure that special agents assigned to the Presidential Protective Division and the Vice Presidential Protective Division reach annual training targets given current and planned staffing levels. The agency concurred with our recommendation but told us that the agency no longer agreed with the training target and planned to reevaluate it as of May 2019. Consequently, Secret Service reported that the Office of Protective Operations solicited training requirements from each internal operational division, including the Presidential and Vice Presidential Protective Divisions, to determine the appropriate amount of training and associated training hours for each division. These training requirements informed the Secret Service's August 2021 Human Capital Strategic Plan, including information on staffing needed to meet stated training requirements. This plan sets new annual training targets for special agents assigned to PPD and VPD to be approximately 12 percent. However, in September 2021, Secret Service officials told us that they did not anticipate being able to meet the new training target until they reach planned staffing level targets in fiscal year 2025. These additional actions addressed a portion of our recommendation, specifically reaching annual training targets given planned staffing levels in 2025. In May 2022, March 2023, and August 2024, Secret Service provided us with updated training data regarding time PPD and VPD special agents spent in training. In each update, time spent in training was still far below their target of 12 percent. For example, between October 2023 and August 2024, PPD and VPD special agents spent 5.2 percent and 2.6 percent of their time in training, respectively. Of note, these August 2024 figures were lower than when we made the recommendation in May 2019. Secret Service expected that these training levels would remain steady or decrease in FY2025 due to the administration change. The August 2024 update to the Secret Service training plan states that personnel levels remain below its planned targets. Specifically, Secret Service was staffed to 84 percent of its target as of August 2024, which equated to a shortage of 1,525 employees based on goals specified in the Secret Service's Human Capital Strategic Plan. In February 2025, Secret Service reported that the agency was revising staffing requirements again, in response to the assassination attempt of Donald Trump during the 2024 Presidential campaign, and the enactment of the Enhanced Presidential Security Act of 2024. Secret Service officials told us that prior staffing and training levels have been at less-than-optimal levels for PPD and VPD special agents. To fully implement this recommendation, the Secret Service needs to develop and implement a plan to ensure that special agents assigned to PPD and the VPD reach annual training targets given current and planned staffing levels. In the meantime, affected special agents may continue to lack training required to prevent security breaches, such as that of September 19, 2014, when an intruder jumped the north fence and entered the White House. Trained special agents are critical to ensuring the safety and security of presidents and other protectees, as underscored by the July 2024 assassination attempt of former President Trump.
|
| United States Secret Service |
Priority Rec.
The Director of the Secret Service should develop and implement a policy that documents the process for collecting complete Uniformed Division officer training data and establishes the types of information that should be collected. (Recommendation 2) |
In May 2019, we reported that training data collected on the Secret Service's Uniform Division were incomplete and in certain cases unrelated to protection or lacked descriptions to clearly link the training to required skills. Further, the process used to capture the data was not consistently employed and did not include information on how or whether to capture internal on-the-job training instances, or instruction on the type of training to be captured to demonstrate that the training is protection-related training. We therefore recommended that the Director of the Secret Service develop and implement a policy that documents the process for collecting complete Uniformed Division officer training data and establishes the types of information that should be collected. The Secret Service, through DHS, concurred with our recommendation, stating that it would develop rigorous and uniform standards for collecting and reporting training data related to the Uniformed Division branch, and would work to capture additional training information. In September 2020, Secret Service officials reported that it upgraded the Performance and Learning Management System (PALMS) for purposes of tracking training records and training targets in a more efficient and streamlined process for all Uniformed Division officer training. According to Secret Service officials, this tracking includes the Field Officer Training and the on-the-job training programs for Uniformed Division officers. In addition, the Secret Service reports to have created 18 checklists that bundle, categorize, and outline the types of training required for Uniformed Division officers. Secret Service officials also report to have created a draft policy that documents the process for collecting complete Uniformed Division officer training data and establishes the types of information that should be collected. In June 2021, Secret Service provided us with a draft of this policy that would, among other things, formalize how all on-the-job training should be recorded and certified. Since then, in March 2023, Secret Service informed us that PALMS was no longer being used to track training records and targets, noting that DHS had "decommissioned" the system. Secret Service stated that, due to the decommissioning of the PALMS system, Uniformed Division training policies are currently "on hold." In July 2024, Secret Service reported that the policies had not yet been finalized, and stated that its new anticipated date for finalizing the policies is September 30, 2024. In February 2025, Secret Service's policy had been finalized. The policy, published in January 2025, defines roles and responsibilities related to Uniformed Division training, and specifies the training courses that UD officers must complete, including the number of hours spent on each training topic, in a biennial training plan. However, the policy does not document how data is to be collected to demonstrate that UD officers have completed the training, along with the type of information that should be collected. To fully implement this recommendation, the Secret Service needs to document the process for collecting complete UD officer training data, including the type of training-related information that should be collected. We will continue to monitor the Secret Service's progress in implementing this recommendation.
|
