Railroad Safety: Quiet Zone Analyses and Inspections Could Be Improved
Highlights
What GAO Found
GAO found that the benefits of quiet zones—–i.e., highway-rail at-grade crossings (grade crossings) where train horns are not sounded—have not been quantified and that the costs to establish quiet zones vary. The Federal Railroad Administration's (FRA) train horn regulations allow public authorities (e.g., cities or towns) the opportunity to establish quiet zones if they install safety measures that reduce risks associated with the absence of the train horn (see fig.). While GAO did not identify any research that has quantified the benefits of quiet zones, most stakeholders GAO interviewed said that these quiet zones provide benefits to communities, such as reducing noise or increasing economic development. According to FRA guidance, the factors that affect the costs to establish quiet zones can vary based on the number of grade crossings and types of safety measures used. Public authorities, which typically incur the costs and receive the benefits of quiet zones, must therefore decide whether the benefits of quiet zones exceed the costs.
Examples of the Federal Railroad Administration's Approved Quiet Zone Safety Measures
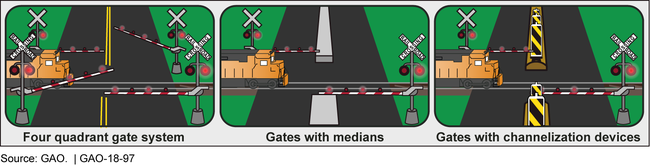
To evaluate the effectiveness of its train horn regulations, FRA has analyzed data on grade crossings in quiet zones and is transitioning to a formal process for inspecting quiet zones.
- Analyses: FRA's analyses showed grade crossings in quiet zones were generally as safe as they were when train horns were sounded. However, these analyses did not control for changes to grade crossings' characteristics over time—–e.g., train speeds or frequency. Such changes may decrease the analyses' reliability. A revised methodology that accounts for these changes could provide FRA with better information on the long-term effects of the train horn regulations, including the safety of quiet zones.
- Inspections: Recognizing the need for additional oversight, FRA has taken steps to formalize its process for inspecting quiet zones. FRA has primarily relied on public authorities to oversee quiet zones and ensure compliance with the train horn regulations, in addition to informal inspections by FRA's Grade Crossing Managers. In September 2017, FRA began conducting formal inspections of quiet zones using Grade Crossing Inspectors. However, FRA has not developed guidance for how inspections are to be conducted, including how frequently inspections are to be performed or what should be examined. Without guidance, FRA cannot ensure that inspections are being conducted consistently across FRA's eight regions.
Why GAO Did This Study
Accidents at grade crossings are a major source of fatalities in the railroad industry. FRA—the federal agency responsible for providing regulatory oversight of grade-crossing safety—–issued regulations on the use of train horns in 2005. Railroads generally support sounding the horn, whereas, communities often support quiet zones to reduce noise.
Congress included a provision in statute for GAO to examine FRA's train horn regulations, including those on quiet zones. Among other things, this report: (1) describes benefits and costs of quiet zones, and (2) examines how FRA evaluates the effectiveness of its train horn regulations. GAO analyzed FRA's documentation on quiet zones, including FRA's train horn regulations and 2011 and 2013 studies on quiet zone safety; reviewed literature; and interviewed FRA program officials in headquarters, Grade Crossing Managers in FRA's 8 regions, and a nongeneralizable sample of another 32 stakeholders from 6 states, railroads, public authorities, and private industry consulting firms. State and public authorities were selected based on the number of quiet zones, geographic diversity, and FRA's recommendations.
Recommendations
GAO recommends that FRA: (1) revise its methodology for analyzing the safety of quiet zones, and (2) develop guidance on conducting quiet zone inspections. The Department of Transportation partially concurred with the first recommendation, saying it would consider it, and fully concurred with the second. GAO continues to believe changes to the methodology are needed, as discussed in the report.
Recommendations for Executive Action
| Agency Affected | Recommendation | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Federal Railroad Administration | The Administrator of FRA should revise the methodology for the analysis of safety in quiet zones to take into account relevant changes over time--including changes in train and automotive traffic, or in the physical characteristics of the grade crossing. (Recommendation 1) |
The Federal Railroad Administration (FRA) is responsible for providing regulatory oversight of the safety of both freight and passenger railroads. FRA also has specific responsibilities related to the safety of grade crossings-where railroad tracks cross roads-including issuing regulations regarding the use of train horns at grade crossings. Federal regulations require that train horns be sounded in advance of all public grade crossings. However, the regulations also provide an opportunity for public authorities to reduce the effects of noise associated with the train horns by establishing quiet zones-i.e., grade crossings where train horns are not routinely sounded when approaching the grade crossings. Communities often support quiet zones to reduce noise, whereas railroads generally support sounding the horn. In 2017, GAO reported that, to evaluate the effectiveness of its train horn regulations, FRA had analyzed data on grade crossings in quiet zones. FRA's analyses showed grade crossings in quiet zones were generally as safe as the same grade crossings when train horns were sounded. However, FRA's methodology for analyzing the safety of grade crossings in quiet zones did not control for changes to grade crossings' characteristics over time including changes in train and automotive traffic. GAO reported that not controlling for such changes could decrease the analyses' reliability over time because FRA's methodology did not control for relevant changes to grade crossings in quiet zones. By continuing to rely on this methodology, FRA may be missing an opportunity to ensure that established quiet zones are providing the same level of safety as when train horns were sounded. As a result, GAO recommended that FRA revise the methodology for the analysis of safety in quiet zones to take into account relevant changes over time-including changes in train and automotive traffic. In 2019, GAO confirmed that FRA revised its methodology for analyzing safety in quiet zones, which accounted for relevant changes over time. Specifically, FRA provided GAO with a report detailing FRA's improved methodology for assessing quiet zone safety. FRA's new methodology analyzes the relative safety of grade crossings in quiet zones compared to similar grade crossings where the train horn is sounded, using a bucket analysis that considers train and motor vehicle traffic. To perform this analysis, FRA groups-buckets-grade crossings in quiet zones and compares them to grade crossings where the train horn is sounded with similar motor vehicle and train traffic levels. FRA's analysis showed that grade crossings in quiet zones with less motor vehicle and train traffic experience relatively more incidents than similar grade crossings where the train horn is sounded. The analysis also found that grade crossings in quiet zones with more motor vehicle and train traffic experienced relatively fewer incidents than similar grade crossings where the train horn is sounded. As a result of these findings, FRA concluded it cannot establish whether quiet zones are as safe as grade crossings where the train horn is sounded. FRA also plans to repeat its analysis every two years and to compare evidence over time to better assess the safety of quiet zones. It is clear that FRA's new methodology had a direct and substantial impact on its ability to determine the safety of quiet zones. FRA's continued use of this or a similar methodology will better position the agency to obtain the reliable information it needs to oversee quiet zone safety and more fully analyze the safety of quiet zones, which will help reduce the risks to railroads, motorists, and others that use such grade crossings.
|
| Federal Railroad Administration | The Administrator of FRA should develop guidance for Inspectors on the nature and frequency of quiet zone inspections. (Recommendation 2) |
The Federal Railroad Administration (FRA) is responsible for providing regulatory oversight of the safety of both freight and passenger railroads. FRA also has specific responsibilities related to the safety of grade crossings, including issuing regulations regarding the use of train horns at grade crossings. Grade crossings are where railroad tracks cross roads. Federal regulations require that train horns be sounded in advance of all public grade crossings. However, the regulations also provide an opportunity for public authorities to reduce the effects of noise associated with the train horns by establishing quiet zones. In 2017, GAO reported that, to evaluate the effectiveness of its train horn regulations, FRA had analyzed data on grade crossings in quiet zones and was transitioning to a formal process for inspecting quiet zones. Recognizing the need for additional oversight, FRA had taken steps to formalize its process for inspecting quiet zones. FRA had primarily relied on public authorities to oversee quiet zones and ensure compliance with the train horn regulations, in addition to informal inspections by FRA's Grade Crossing Managers. In September 2017, FRA began conducting formal inspections of quiet zones using Grade Crossing Inspectors. However, FRA had not developed guidance for how inspections were to be conducted, including how frequently inspections were to be performed or what should be examined. Without this guidance, FRA could not ensure that inspections were being conducted consistently across FRA's eight regional offices. As a result, GAO recommended that FRA develop guidance for inspectors on the nature and frequency of quiet zone inspections. In 2018, GAO confirmed that FRA issued guidance for inspection of quiet zones that addressed both the frequency and the nature of such inspections. For example, the guidance specifies that new quiet zones are to be inspected within 60 days of the date they are established and existing quiet zones are to be inspected every 3 years, at a minimum, to verify they continue to comply with federal regulations. The guidance also includes a quiet zone inspection checklist that inspectors are expected to complete during the quiet zone inspection. The checklist includes information such as the location of the quiet zone, the type of grade crossings in the zone (e.g. public highway-rail, private highway-rail), and safety improvements in the quiet zone. It also includes information on inspector recommendations for safety improvements and corrective actions that are needed. FRA distributed both the checklist and the instructions for preparing the checklist to applicable staff in August 2018. These actions substantially clarify when inspections are to be performed and the type of information to be collected during inspections. It should also significantly improve the consistency of information collected across FRA regional offices and better facilitate nationwide analyses of both quiet zone compliance with regulations and types of problems being experienced at quiet zones. With these actions, FRA has now reasonable assurance that inspections are being conducted consistently across FRA's eight regions and as FRA intends.
|
