Broadband: Observations on Past and Ongoing Efforts to Expand Access and Improve Mapping Data
Fast Facts
The telecommunications industry and the federal government have spent hundreds of billions of dollars to expand broadband across the U.S. While broadband is available in most urban areas, about 1 in 4 people in rural areas lack access, according to recent data.
In 2019, the Federal Communications Commission and Department of Agriculture started new, multi-year broadband support programs intended to increase access in rural and tribal areas to reduce this digital divide. The FCC proposed a new mapping effort to target funding where it’s most needed. Coordinating the agencies’ work to avoid overlap will be critical to closing access gaps.
[Text updated to correct data on rural access.]

teleworking
Highlights
What GAO Found
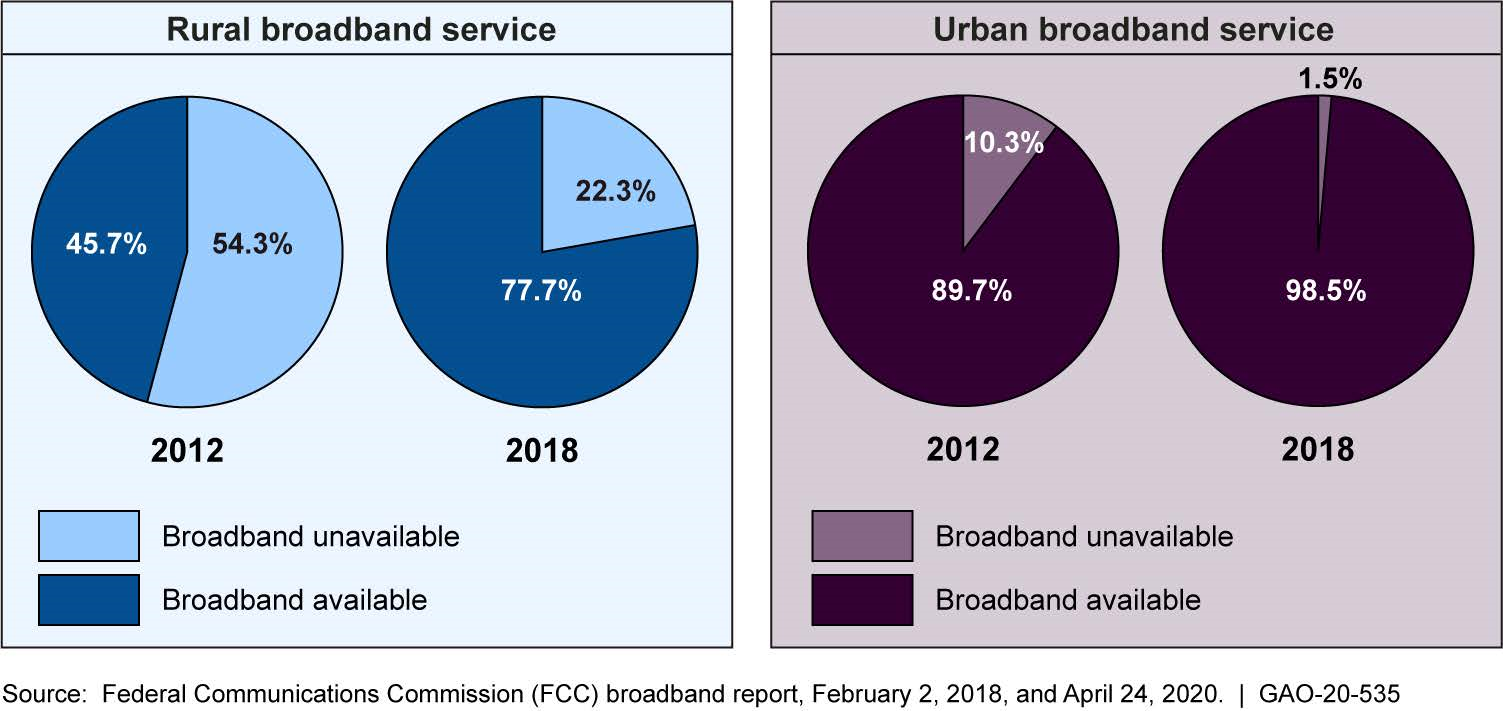
Telecommunications industry and federal government investments have expanded access to broadband in the United States. From 2009 through 2017, the industry made capital investments of about $795 billion, including investments in broadband infrastructure, according to U.S. Census Bureau survey data. Federal investments totaled about $47.3 billion to target broadband infrastructure for rural areas over the same time, according to data from the Federal Communications Commission (FCC), the Rural Utilities Service (RUS), and the National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA). FCC's Universal Service Fund high-cost program expanded service to about 2.3 million residential and small business locations, mostly from 2015 through 2017, according to data FCC collects from providers. FCC reported that fixed broadband service was available to 94.4 percent of the U.S. population in 2018, up from 81.2 percent in 2012, although affordability and digital literacy remain barriers to adoption and use. While service availability for people in rural areas increased from 45.7 percent in 2012 to 77.7 percent in 2018, service in rural areas continues to lag behind urban areas, according to FCC's broadband availability report (see figure).
Comparison of Fixed Broadband Availability in Rural and Urban Areas at the Speed of 25 Megabits per Second (Mbps) Upload and 3 Mbps Download, 2012 and 2018
FCC and RUS have taken actions to address deployment challenges, such as taking steps to improve their ability to pinpoint where gaps in broadband deployment still exist. In August 2019, FCC proposed an initiative to change how it collects broadband deployment data, with the goal of using a new methodology to improve data accuracy and FCC's ability to target funds to locations that lack access. FCC and RUS have also coordinated on broadband deployment issues. For example, to avoid funding areas where broadband service is already deployed, agency officials regularly communicate on information about where their broadband deployment programs are funding new deployments. Continued communication and coordination on topics such as collecting and using improved data will be especially important in assuring that federal dollars are effectively targeted as agencies' efforts to improve mapping and target resources progress.
Why GAO Did This Study
Broadband is critical for economic, educational, and personal uses. Industry and federal investments have made broadband available to the vast majority of Americans. For example, FCC's high-cost program provides funding to broadband providers to deploy broadband in rural, insular, and high-cost areas. However, some rural areas continue to lack access due, in part, to challenges with providing service to areas where deployment costs are high and returns on investment are low.
GAO was asked to examine the current state of broadband investment and deployment. This report examines (1) industry and federal investments to deploy broadband in the United States since 2009, and (2) efforts federal agencies are making to address deployment challenges.
GAO analyzed industry and federal government data from 2009 through 2017 or 2018 (the most recent year of available data) on broadband investments and deployment; reviewed statutes and regulations, rulemaking proceedings, and FCC, RUS, and NTIA program information; interviewed federal officials; and obtained information about deployment challenges from interviews with 32 industry, academic, and consumer stakeholders, including 16 broadband providers selected to represent a range of provider sizes and types of technologies.
Recommendations
In prior work, GAO recommended that FCC improve its mapping data and RUS better manage its broadband programs. The agencies have addressed some, but not all, of the recommendations. FCC and RUS reviewed a draft of this report and provided technical comments.
