Information Technology: Effective Practices Have Improved Agencies' FITARA Implementation
Fast Facts
To reform government-wide information technology management, Congress enacted the Federal Information Technology Acquisition Reform Act (commonly referred to as FITARA) in 2014.
What practices have federal agencies put in place to implement the law?
We reviewed nine agencies and found 12 practices officials said helped them to effectively implement one or more of the FITARA provisions.
For example, five of the agencies said that centralizing the management of software licenses was essential to meeting the software purchasing provision of the law. By doing so, agencies were able to make agency-wide purchasing decisions that saved them money.

Graphic of the U.S. Capitol over a photo of paper money
Highlights
What GAO Found
Nine selected agencies (the Departments of Agriculture, Commerce, Health and Human Services, Homeland Security, Justice, and Veterans Affairs; the Agency for International Development; the National Aeronautics and Space Administration; and the General Services Administration) identified 12 practices that helped them to effectively implement one or more Federal Information Technology Acquisition Reform Act provisions (commonly referred to as FITARA). The following figure identifies the 12 practices, including the four overarching ones, considered vital to implementing all provisions.
Figure: Practices for Effectively Implementing Federal Information Technology Acquisition Reform Act (FITARA)
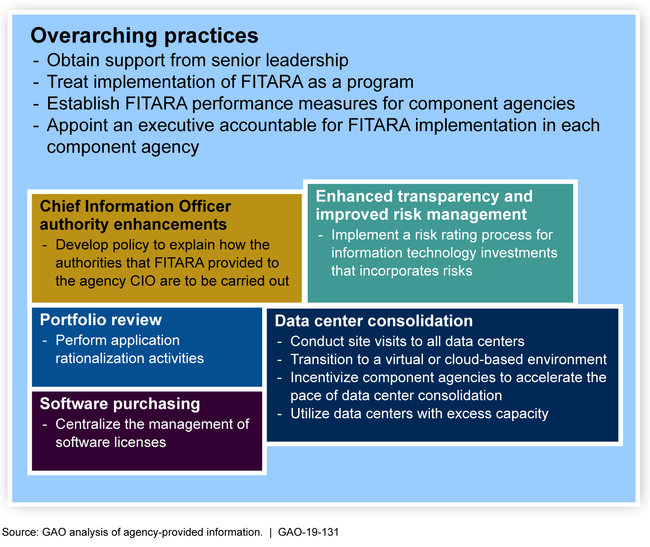
By applying the overarching practices, covered agencies were better positioned to implement FITARA. In addition, by implementing the practices relative to the five FITARA provisions GAO selected, covered agencies realized information technology (IT) management improvements, such as decommissioning old systems and cost savings.
Why GAO Did This Study
Congress has long recognized that IT has the potential to enable federal agencies to accomplish their missions more quickly, effectively, and economically. However, fully exploiting this potential has presented challenges to covered agencies, and the federal government's management of IT has produced mixed results.
As part of its effort to reform the government-wide management of IT, in December 2014 Congress enacted FITARA. The law included specific requirements related to enhancing Chief Information Officers' (CIO) authorities, improving the risk management of IT investments, reviewing agencies' portfolio of IT investments, consolidating federal data centers, and purchasing software licenses. GAO has reported numerous times on agencies' effectiveness in implementing the provisions of the law and highlighted agencies that have had success in implementing selected provisions.
In this report, GAO identifies practices that agencies have used to effectively implement FITARA. GAO selected five provisions of FITARA to review: (1) CIO authority enhancements; (2) enhanced transparency and improved risk management; (3) portfolio review; (4) data center consolidation; and (5) software purchasing. GAO then selected nine agencies that had success in implementing at least one of the five provisions. GAO compiled practices where at least one agency was better positioned to implement a provision or realized an IT management improvement or cost savings.
For more information, contact Carol C. Harris at (202) 512-4456 or harriscc@gao.gov.
