Federal Timber Sales: Forest Service and BLM Should Review Their Regulations and Policies Related to Timber Export and Substitution
Fast Facts
The Forest Service and Bureau of Land Management sell millions of dollars of timber from federal forests each year. Federal law bans buyers from exporting unprocessed timber from western federal lands, along with related practices. Some agency policies to implement the ban are outdated or unclear. The agencies have also not issued required regulations.
While the agencies found no violations of the ban in the past decade, several officials said there might be a risk of future violations if, for example, log prices go up or demand increases.
We recommended that the agencies review their regulations and policies related to timber export.
Federal Lands West of the 100th Meridian
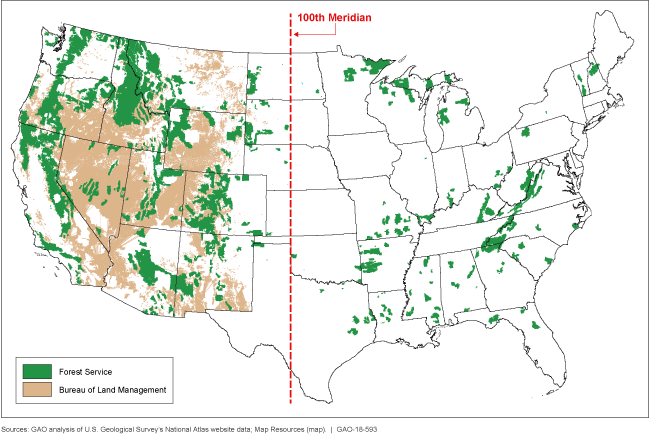
Map showing the 100th meridian—exporting unprocessed federal timber cut from federal lands west of this line is banned.
Highlights
What GAO Found
The Forest Service, within the Department of Agriculture, and the Bureau of Land Management (BLM), within the Department of the Interior, found no violations of the ban on federal timber export and substitution from 2007 through 2017, according to agency documents and officials. All agency officials and stakeholders GAO interviewed said the likelihood of illegal timber export and substitution is low, citing several reasons, including economic factors associated with log markets, which have changed over the years. For example, many officials and stakeholders said the timber harvested from federal lands is smaller and of lower quality compared to what was harvested in the 1990s, making it less likely to be exported.
The Forest Service and BLM did not issue new regulations related to illegal federal timber export and substitution, and some agency policies related to export and substitution are outdated or unclear. The agencies did not issue regulations to implement the Forest Resources Conservation and Shortage Relief Act of 1997, as required by the act. Without issuing new regulations or obtaining legislative relief from this requirement, the agencies will continue to be out of compliance with the act. The agencies have policies to help prevent, detect, and respond to illegal timber export and substitution, such as policies that require the marking of logs to identify them as coming from federal lands. However, the agencies have not reviewed their policies for continued relevance and effectiveness as called for by federal standards for internal control, and some policies are outdated or unclear. For example, Forest Service policy calls for the collection of a certification form to help determine whether timber purchasers are engaged in export or substitution, but the form expired in 1999. Also, it is unclear what BLM considers a violation of the export ban because agency policy does not define what constitutes a violation. Forest Service officials said the agency has not reviewed its policies since 1997, largely due to competing priorities, but agreed it would be beneficial to do so. BLM officials said they reviewed the agency's export regulations in 2010, but this effort did not include a review of timber export policies. By reviewing agency policies and making changes as necessary, the agencies will have better assurance that their policies are relevant and effective for addressing the risk of illegal timber export and substitution.
Logs at an Export Facility; Logs on a Truck

Why GAO Did This Study
Each year, the federal government sells millions of dollars of timber from federal forests. Federal law generally prohibits the export of unprocessed logs harvested from federal lands in the western United States. It also prohibits substitution of federal logs for privately sourced timber in domestic mills when the privately sourced timber is exported without processing.
GAO was asked to examine the issue of illegal federal timber export and substitution. This report (1) describes the extent to which the Forest Service and BLM identified violations of the timber export and substitution ban that occurred from 2007 through 2017 and the likelihood of violations and (2) examines the agencies' regulations, policies, and practices to help prevent, detect, and respond to illegal timber export and substitution.
GAO reviewed laws, regulations, and policies regarding illegal timber export and substitution; compared agency regulations with laws, and agency policies with federal internal control standards; and interviewed agency officials and stakeholders—such as trade groups and state officials— selected to provide a range of perspectives.
Recommendations
GAO recommends that the Forest Service and BLM issue new regulations or seek legislative relief from the requirement to do so, and review their policies for relevance and effectiveness and issue new policies as necessary. The agencies generally agreed with GAO's recommendations.
Recommendations for Executive Action
| Agency Affected | Recommendation | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Forest Service | The Chief of the Forest Service should determine whether new regulations governing timber export and substitution are appropriate. If the agency determines new regulations are appropriate, it should issue them in accordance with the 1997 act, in consultation with BLM. Otherwise, the agency should seek legislative relief from the act's requirement. (Recommendation 1) |
In its fiscal year 2023 budget justification, issued March 2022, the Forest Service sought legislative relief from the requirement to issue new regulations to implement the 1997 Act. Specifically, the Forest Service requested that the following language be included in agency appropriations: "The Secretary of Agriculture shall not be required to issue regulations under section 495 of the Forest Resources Conservation and Shortage Relief Act of 1997 (16 U.S.C. 620f) for the fiscal year ending September 30, 2023." As a result, we consider this recommendation closed.
|
| Bureau of Land Management | The Director of the BLM should determine whether new regulations governing timber export and substitution are appropriate. If the agency determines new regulations are appropriate, it should issue them in accordance with the 1997 act, in consultation with the Forest Service. Otherwise, the agency should seek legislative relief from the act's requirement. (Recommendation 2) |
BLM issued a Final Rule addressing timber export, titled "Forest Management Decision Protest Process and Timber Sale Administration," which was published in the Federal Register in December 2020 and finalized in January 2021. BLM stated that it met with and updated the Forest Service periodically to confirm that both agencies are interpreting the Timber Shortage Relief Act of 1990 similarly.
|
| Forest Service | The Chief of the Forest Service should review agency policies for continued relevance and effectiveness in addressing the risk of illegal timber export and substitution, and based on that review--and in accordance with applicable regulations--should issue new policies as necessary. (Recommendation 3) |
In December 2021, the Forest Service stated that the agency completed a comprehensive review of agency policies and timber sale contracts. Based on this review, in July 2022, the agency finalized revisions of certain timber management policies--including policies related to timber export-- in Chapter 20, of the Forest Service Timber Handbook. As a result, we consider this recommendation closed as implemented.
|
| Bureau of Land Management | The Director of the BLM should review agency policies for continued relevance and effectiveness in addressing the risk of illegal timber export and substitution, and based on that review--and in accordance with applicable regulations--should issue new policies as necessary. (Recommendation 4) |
In August 2023, BLM developed policies to incorporate its January 2021 Final Rule addressing illegal timber export and substitution, including manuals and handbooks that contain timber-related provisions. For example, the handbook relating to timber sale conduct provides the procedures for determining bidder qualifications, including the requirement that bidders are non-exporting. As a result, we consider this recommendation closed as implemented.
|
