Central States Pension Fund: Investment Policy Decisions and Challenges Facing the Plan
Highlights
What GAO Found
The Central States, Southeast and Southwest Areas Pension Fund (CSPF) was established in 1955 to provide pension benefits to trucking industry workers, and is one of the largest multiemployer plans. According to its regulatory filings, CSPF had less than half the estimated funds needed to cover plan liabilities in 1982 at the time it entered into a court-enforceable consent decree that provides for oversight of certain plan activities. Since then, CSPF has made some progress toward achieving its targeted level of funding; however, CSPF has never been more than 75 percent funded and its funding level has weakened since 2002, as shown in the figure below.
CSPF Funding Levels and Active and Nonworking Participant Totals, 1982–2016
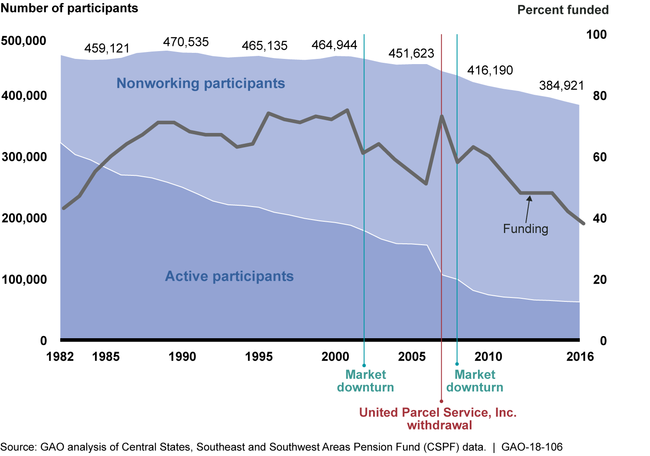
Note: The most recent, publicly available data were from 2016. End-of-year participant data and beginning-of-year funding data are presented at the closest year end.
Stakeholders GAO interviewed identified numerous factors that contributed to CSPF's financial condition. For example, stakeholders stated that changes within the trucking industry as well as a decline in union membership contributed to CSPF's inability to maintain a healthy contribution base. CSPF's active participants made up about 69 percent of all participants in 1982, but accounted for only 16 percent in 2016. The most dramatic change in active participants occurred in 2007 when the United Parcel Service, Inc. (UPS) withdrew from the plan. At that time, UPS accounted for about 30 percent of the plan's active participants (i.e. workers). In addition, the market declines of 2001 to 2002 and 2008 had a significant negative impact on the plan's long-term investment performance. Stakeholders noted that while each individual factor contributed to CSPF's critical financial condition, the interrelated nature of the factors also had a cumulative effect on the plan's financial condition.
Both CSPF's investment policy and the process for setting and executing it have changed several times since the consent decree was established in 1982. The original consent decree gave an independent asset manager—called a named fiduciary—exclusive authority to set and change the plan's investment policies and manage plan assets, and prohibited CSPF trustees from managing assets or making investment decisions. Initially, the named fiduciaries sold the troubled real estate assets acquired during the pre-consent decree era. Subsequent changes include the following:
In 1993, the named fiduciaries started to increase investment in equities, and their policies continued to direct that asset allocations be weighted toward equities until early 2017.
Between 2003 and 2010, the court approved three plan decisions to move a total of 50 percent of CSPF's assets into passively-managed accounts (passive management typically seeks to match the performance of a specific market index and reduce investment fees).
An early-2017 investment policy change precipitated by CSPF's deteriorating financial condition will continue to move plan assets into fixed income investments ahead of projected insolvency, or the date when CSPF is expected to have insufficient assets to pay promised benefits when due. As a result, assets will be gradually transitioned from “return-seeking assets”—such as equities and emerging markets debt—to high-quality investment grade debt and U.S. Treasury securities with intermediate and short-term maturities. The plan is projected to become insolvent on January 1, 2025. CSPF officials and named fiduciary representatives said these changes are intended to reduce the plan's exposure to market risk and volatility, and provide participants greater certainty prior to projected insolvency.
GAO found that CSPF's investment returns and expenses were generally in line with similarly sized institutional investors and with demographically similar multiemployer pension plans. For example, GAO's analysis of returns using the peer group measure used by CSPF known as the Wilshire Associates' Trust Universe Comparison Service (TUCS), showed that CSPF's annual investment returns since 1995 were above the median about as many times as they were below. Similarly, comparing CSPF's returns to a peer group of similar multiemployer defined benefit plans using federally required annual reports found that CSPF's annual investment returns were in line with those of its peers. Specifically, CSPF's annual returns were above the median nine times and below it six times—and CSPF's overall (dollar-weighted) average annual return from 2000 through 2014 was close to that of the peer median average return of 4.8 percent.
In addition, GAO found that CSPF's investment fees and other administrative expenses have also been in line with other large multiemployer plans. For example:
CSPF's investment fees as a percentage of assets were about 9 percent lower than the median of large defined benefit multiemployer plans over the 2000 through 2014 period—though much of that difference is accounted for by a relative reduction in investment fees since 2007. CSPF's investment fees as a percentage of assets were, on average, about 34 basis points (or 0.34 percent).
CSPF's administrative expenses related to the day-to-day operations of the plan have also been in line with other large multiemployer plans. CSPF's administrative expenses per participant were below the median for large defined benefit multiemployer plans for 12 of the 15 years over the 2000 through 2014 period. As of 2014, CSPF's administrative expense was $98 per participant, which is about 16 percent less than the median for large defined benefit multiemployer plans.
Why GAO Did This Study
Multiemployer plans are collectively bargained pension agreements often between labor unions and two or more employers. CSPF is one of the nation's largest multiemployer defined benefit pension plans, covering about 385,000 participants. Since 1982, the plan has operated under a court-enforceable consent decree which, among other things, requires that the plan's assets be managed by independent parties. Within 7 years, CSPF estimates that the plan's financial condition will require severe benefit cuts. GAO was asked to review the events and factors that led to the plan's critical financial status and how its investment outcomes compare to similar plans.
GAO describes (1) what is known about the factors that contributed to CSPF's critical financial condition; (2) what has been CSPF's investment policy, and the process for setting and executing it, since the consent decree was established; and (3) how CSPF's investments have performed over time, particularly compared to similar pension plans.
GAO reviewed relevant federal laws and regulations; interviewed CSPF representatives, International Brotherhood of Teamsters officials and members, federal officials, and knowledgeable industry stakeholders; reviewed CSPF documentation including investment policy statements and board of trustee meeting minutes; and analyzed investment returns and fees from required, annual pension plan filings and from consultant benchmarking reports.
Recommendations
GAO is not making recommendations in this report.
Brief History of the Consent Decree
In the 1970s, the U.S. Department of Labor (DOL), the Internal Revenue Service, and the U.S. Department of Justice investigated CSPF for alleged fiduciary breaches of requirements in the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974 (ERISA). As a result of its investigation, DOL filed suit against former trustees of the plan, and, in September 1982, the parties entered into a court-enforceable consent decree. The consent decree provides measures to ensure that CSPF complies with the requirements of ERISA and allows for oversight of certain plan activities. The consent decree has been amended several times and currently remains in force.
