Antibiotic Resistance: More Information Needed to Oversee Use of Medically Important Drugs in Food Animals
Fast Facts
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria are one of the biggest threats to global health, sickening an estimated 2 million people in the United States each year. There is strong evidence that some resistance in bacteria is caused by antibiotic use in food animals (cattle, poultry, swine).
We found gaps in FDA's oversight of antibiotic use in food animals and USDA’s and HHS’s data collection, among other things. For example, they lack farm-specific data, do not have metrics to assess their actions to manage antibiotics use, and have not conducted on-farm investigations during foodborne illness outbreaks.
We made recommendations to address these concerns.
How Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria Can Develop and Spread
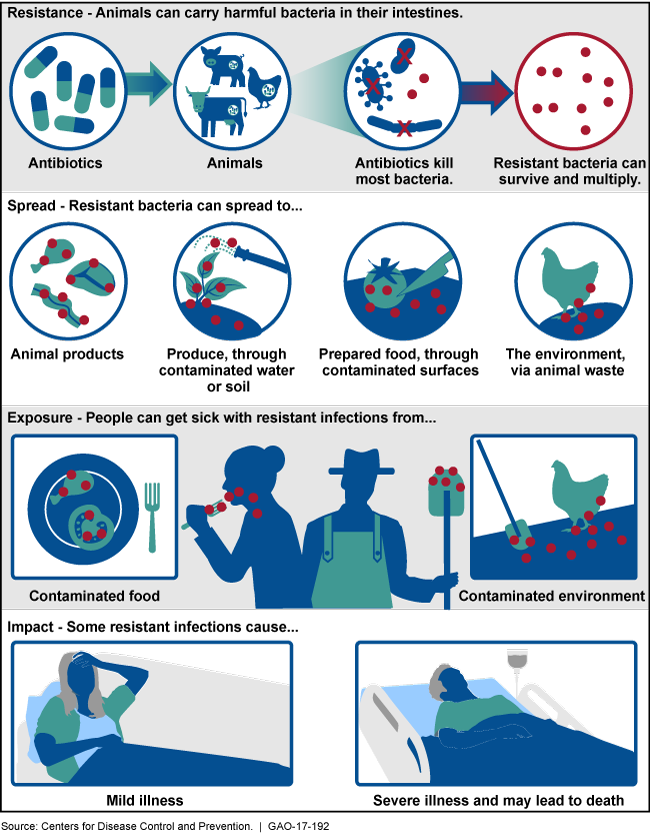
Illustration of how antibiotic-resistant bacteria can develop, spread, and impact humans
Highlights
What GAO Found
Since 2011, when GAO last reported on this issue, the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) has increased veterinary oversight of antibiotics and, with the Department of Agriculture (USDA), has made several improvements in collecting data on antibiotic use in food animals and resistance in bacteria. For example, HHS's Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued a regulation and guidance for industry recommending changes to drug labels. However, oversight gaps still exist. For example, changes to drug labels do not address long-term and open-ended use of antibiotics for disease prevention because some antibiotics do not define duration of use on their labels. FDA officials told GAO they are seeking public comments on establishing durations of use on labels, but FDA has not clearly defined objectives for closing this gap, which is inconsistent with federal internal control standards. Without doing so, FDA will not know whether it is ensuring judicious use of antibiotics. Moreover, gaps in farm-specific data on antibiotic use and resistance that GAO found in 2011 remain. GAO continues to believe HHS and USDA need to implement a joint on-farm data collection plan as previously recommended. In addition, FDA and USDA's Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (APHIS) do not have metrics to assess the impact of actions they have taken, which is inconsistent with leading practices for performance measurement. Without metrics, FDA and APHIS cannot assess the effects of actions taken to manage the use of antibiotics.
Three selected countries and the European Union (EU), which GAO reviewed, have taken various actions to manage use of antibiotics in food animals, including strengthening oversight of veterinarians' and producers' use of antibiotics, collecting farm-specific data, and setting targets to reduce antibiotic use. The Netherlands has primarily relied on a public-private partnership, whereas Canada, Denmark, and the EU have relied on government policies and regulations to strengthen oversight and collect farm-specific data. Since taking these actions, the use or sales of antibiotics in food animals decreased and data collection improved, according to foreign officials and data reports GAO reviewed. Still, some U.S. federal officials and stakeholders believe that similar U.S. actions are not feasible because of production differences and other factors.
HHS and USDA officials said they have not conducted on-farm investigations during foodborne illness outbreaks including those from antibiotic-resistant bacteria in animal products. In 2014, USDA agencies established a memorandum of understanding to assess the root cause of foodborne illness outbreaks. However, in 2015 in the agencies' first use of the memorandum, there was no consensus among stakeholders on whether to conduct foodborne illness investigations on farms and the memorandum does not include a framework to make this determination, similar to a decision matrix used in other investigations. According to a directive issued by USDA's Food Safety and Inspection Service, foodborne illness investigations shall include identifying contributing factors and recommending actions or new policies to prevent future occurrences. Developing a framework, in coordination with HHS's Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and other stakeholders, would help USDA identify factors that contribute to or cause foodborne illness outbreaks, including those from antibiotic-resistant bacteria in animal products.
Why GAO Did This Study
According to the World Health Organization, antibiotic resistance is one of the biggest threats to global health. CDC estimates antibiotic-resistant bacteria cause at least 2 million human illnesses in the United States each year, and there is strong evidence that some resistance in bacteria is caused by antibiotic use in food animals (cattle, poultry, and swine). HHS and USDA are primarily responsible for ensuring food safety, including safe use of antibiotics in food animals. In 2011, GAO reported on antibiotic use and recommended addressing gaps in data collection. GAO was asked to update this information. This report (1) examines actions HHS and USDA have taken to manage use of antibiotics in food animals and assess the impact of their actions, (2) identifies actions selected countries and the EU have taken to manage use of antibiotics in food animals, and (3) examines the extent to which HHS and USDA conducted on-farm investigations of foodborne illness outbreaks from antibiotic-resistant bacteria in animal products.
GAO reviewed documents and interviewed officials and stakeholders. GAO selected three countries and the EU for review because they have taken actions to mitigate antibiotic resistance.
Recommendations
GAO is making six recommendations, including that HHS address oversight gaps, HHS and USDA develop metrics for assessing progress in achieving goals, and USDA develop a framework with HHS to decide when to conduct on-farm investigations. USDA agreed and HHS neither agreed nor disagreed with GAO's recommendations.
Recommendations for Executive Action
| Agency Affected | Recommendation | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Department of Health and Human Services | The Secretary of Health and Human Services should direct the Commissioner of FDA to develop a process, which may include time frames, to establish appropriate durations of use on labels of all medically important antibiotics used in food animals. |
In July 2017, as part of the agency's formal comments, HHS initially neither agreed nor disagreed with the recommendation. Subsequently, in a September 2017 letter, HHS agreed with this recommendation. FDA has taken steps to develop a process for establishing appropriate durations of use on labels of all medically important antibiotics in food animals. FDA published a concept paper in January 2021 and used the concept paper to obtain early input from public comments in June 2021 on a potential framework for how animal drug sponsors could voluntarily make changes to the approved conditions of use for certain medically important antimicrobial drugs to establish a defined duration of use for those indications that currently lack a defined duration of use. According to information provided by FDA, following review of the public comments, the agency intends to work collaboratively with industry to resolve the issue of appropriate durations of use on labels in a science-based manner that is protective of human and animal health. To gather data on dosage regimens, FDA awarded an additional $500,000 grant to fund research projects in fiscal year 2020 aimed to help target and define durations of use for certain medically important antimicrobial drugs approved for use in the feed of food-producing animals. According to information provided by FDA, together these research projects will generate publicly available data, which can be used by sponsors of affected approved animal drug applications to update product dosage regimens and better target when and for how long a drug may be used. In September 2023, FDA issued a draft guidance document for durations of use entitled, "CVM GFI #273 Defining Durations of Use for Approved Medically Important Antimicrobial Drugs Fed to Food-Producing Animals." As of May 2024, FDA accepted public comments on the draft guidance for industry-through January 2024 and received over 4,500 comments, according to FDA. In July 2025, FDA stated that the agency has assessed and incorporated that feedback into the final Guidance for Industry #273, which is in the final stages of FDA clearance. We will provide an update when the agency provides additional information on the finalization of the Guidance for Industry.
|
| Department of Health and Human Services | The Secretary of Health and Human Services should direct the Commissioner of FDA to establish steps to increase veterinary oversight of medically important antibiotics administered in routes other than feed and water, such as injections and tablets. |
In July 2017, as part of the agency's formal comments, HHS initially neither agreed nor disagreed with the recommendation. Subsequently, in a September 2017 letter, HHS agreed with this recommendation. In September 2018, FDA released a broad, five-year plan outlining the activities and important steps it intends to take to support stewardship of medically important antimicrobials in veterinary settings. On June 10, 2021, FDA finalized and published GFI #263 which outlines the process for animal drug sponsors to voluntarily change the approved marketing status of certain medically important antimicrobial drugs from over-the-counter (OTC) to prescription (Rx), for all routes of administration. FDA has requested that animal drug companies voluntarily transition their affected products from OTC to Rx status by June 11, 2023 (i.e., within two years of finalization of GFI #263).
|
| Department of Health and Human Services | The Secretary of Health and Human Services should direct the Commissioner of FDA to develop performance measures and targets for actions to manage the use of antibiotics such as revising the veterinary feed directive and developing guidance documents on judicious use. |
In July 2017, as part of the agency's formal comments, HHS initially neither agreed nor disagreed with the recommendation. Subsequently, in a September 2017 letter, HHS agreed with this recommendation. In August 2020, FDA agreed that performance measures and targets for actions are needed to help gauge the success of antimicrobial stewardship efforts and guide their continued evolution and optimization. In October 2019, FDA announced the availability of performance measures that track the progress of the Center of Veterinary Medicine's (CVM) Five-Year Plan for Supporting Antimicrobial Stewardship in Veterinary Settings. According to FDA, this information is part of FDA-TRACK, a tool that promotes transparency and monitors certain FDA programs through performance measures and projects. FDA's Center of Veterinary Medicine's (CVM) five-year plan is organized under three goals: (1) align antimicrobial drug product use with the principles of antimicrobial stewardship, (2) foster stewardship of antimicrobials in veterinary settings, and (3) enhance monitoring of antimicrobial resistance and antimicrobial drug use in animals. The plan includes goals, actions, and key projects from fiscal years 2019 through 2023. As of June 2021, on its website using FDA-TRACK, the agency highlighted performance measures and targets. For example, one performance measure-the percent of medically important antimicrobial drugs for use in food-producing animals that require oversight of a licensed veterinarian-focuses on compliance with FDA's guidance for industry #213 with a target of 100 percent. According to FDA-TRACK, for this performance measure, 96 percent of drugs sold or distributed in 2019 required veterinary oversight in compliance with FDA's guidance for industry #213. According to officials, FDA-TRACK is updated regularly to keep stakeholders apprised on the agency's progress.
|
| Department of Agriculture | The Secretary of Agriculture should direct the Administrator of APHIS to develop performance measures and targets for collecting farm-specific data on antibiotic use in food animals. |
USDA agreed with this recommendation. In August 2018, the Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (APHIS) stated that it has established performance measures and targets for collecting farm-specific data on antibiotic use in farm animals and antibiotic resistant bacteria. According to the agency's documentation, the performance metrics and targets are: collecting farm-specific data on antimicrobial use from one commodity an average of once per fiscal year, either within a standard National Animal Health Monitoring System (NAHMS) periodic study or via a directed antimicrobial use study. According to officials, APHIS will report farm-specific antimicrobial use data via USDA NAHMS publications (information sheets or interpretive reports) from one commodity each fiscal year.
|
| Department of Agriculture | The Secretary of Agriculture should direct the Administrator of APHIS to develop performance measures and targets for collecting farm-specific data on antibiotic-resistant bacteria in food animals. |
USDA agreed with this recommendation. In August 2018, the Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (APHIS) stated that it has established performance measures and targets for laboratory monitoring of antibiotic resistance of pathogens. According to the agency's documentation and officials, the performance measures and targets are: monitoring antimicrobial susceptibility test data on E. coli, Salmonella, Staphylococcus intermedius, and Mannheimia haemolytica from U.S. populations of cattle, swine, poultry, horses, dogs, and cats; the target is to monitor results from antibiotic susceptibility testing in 3,000 samples per year.
|
| Department of Agriculture | The Secretary of Agriculture should direct the Administrator of APHIS and the Administrator of the Food Safety and Inspection Service to work with the Director of CDC to develop a framework for deciding when on-farm investigations are warranted during outbreaks. |
USDA agreed with this recommendation. In August 2018, USDA's Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (APHIS) stated that it was working closely with USDA's Food Safety and Inspection Service (FSIS) and HHS' Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to develop a framework for deciding when on-farm antimicrobial resistance investigative activities are warranted. In September 2019, according to APHIS officials, the lead agencies, including APHIS, FSIS, and CDC, agreed that it was imperative that cross sector partners from a range of animal agriculture industries be included in developing the framework that was requested in GAO's final report. A framework for making decisions regarding on-farm antimicrobial resistance investigative activities simply will not work without including industry sector partners in the development of the framework, according to APHIS officials. Due to the logistics of getting all of the cross sector partners together, APHIS was unable to schedule the next meeting in the series to develop the Pre-Harvest Framework until December 2019. APHIS anticipated that it would take the remainder of fiscal year 2020 to work through additional meetings with partners and finalize this framework. According to USDA's documentation, the group met at least annually beginning in September 2018 through June 2022. The meetings covered discussion of roles/responsibilities, communication, actions, and next steps, including development of a draft decision matrix and implementation process. According to APHIS officials, the multi-stakeholder group, including APHIS, FSIS, states, and industry groups, continues to meet virtually on a quarterly basis to continue discussions and provide updates on foodborne illness investigations, identify best practices, and research initiatives. Meetings were temporarily interrupted due to the pandemic. Based on these efforts, as of March and June 2022, GAO determined that these pre-harvest meetings with federal, state, and industry partners led by APHIS meets the intent of the recommendation to develop a framework for deciding when on-farm investigations are warranted during outbreaks.
|
