Foreign Aid: U.S. Assistance for the West Bank and Gaza for Fiscal Years 2012-2014
Highlights
What GAO Found
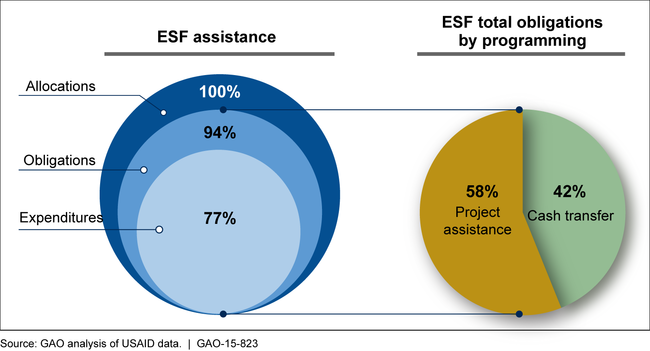
As of June 30, 2015, the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID) had allocated about $1.1 billion of Economic Support Fund (ESF) assistance for the West Bank and Gaza for fiscal years 2012 through 2014, had obligated about $1 billion (94 percent), and had expended about $874 million (77 percent). Project assistance in five development sectors—for example, the water resources and infrastructure sector and the democracy and governance sector—accounted for approximately $619 million of the obligated funds, and cash transfer assistance to the Palestinian Authority (PA) and its creditors accounted for $448 million. Of this amount, $348 million went directly to the PA and then to its creditors and $100 million went directly to its creditors—two Israeli fuel companies, and six hospitals in East Jerusalem—through a line of credit.
U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID) Economic Support Fund (ESF) Assistance for the West Bank and Gaza, Fiscal Years 2012-2014, as of June 2015
GAO found that USAID complied with key requirements included in annual appropriations acts and with its antiterrorism policies and procedures for providing cash transfers to the PA and its creditors. Annual appropriations acts contain various requirements for providing cash transfers to the PA and its creditors, such as ensuring that Congress is notified prior to obligating funds for cash transfers and that funds provided for cash transfers are maintained by the PA in a separate account. For fiscal years 2013 and 2014—the fiscal years in which the PA received cash transfers—GAO examined USAID's determinations of compliance and found that USAID ensured compliance with these key legal requirements. GAO also found that USAID complied with its existing antiterrorism policies and procedures. These policies and procedures require that all PA creditors receiving cash transfer funds are vetted—that is, that the creditors' names and other identifying information are checked against the federal Terrorist Screening Center database and other information sources to determine whether they have links to terrorism. In fiscal years 2013 and 2014, the PA signed cash transfer agreements that affirmed its commitment to prevent the use of transferred funds for financing terrorism. USAID commissioned external audits of funds provided under the fiscal year 2013 cash transfer agreements and did not identify any material instances of PA noncompliance with the agreements or with applicable laws and regulations. USAID reported that, as of June 30, 2015, it had not yet commissioned an external audit that would review the cash transfer agreement for fiscal year 2014.
Why GAO Did This Study
Since 1993, the U.S. government has committed more than $5 billion in bilateral assistance to the Palestinians in the West Bank and Gaza. Assistance to the Palestinians is a key part of the United States' commitment to a negotiated two-state solution to promote peace in the Middle East. USAID is primarily responsible for administering ESF assistance for the West Bank and Gaza.
Congress included a provision in three appropriations acts for GAO to review funds provided through the ESF for the bilateral West Bank and Gaza Program. This report (1) examines the status of USAID's allocations, obligations, and expenditures of ESF assistance to the Palestinians for fiscal years 2012, 2013, and 2014 and (2) assesses the extent to which USAID complied with key legal requirements and its antiterrorism policies and procedures for cash transfers to the PA and its creditors.
GAO reviewed laws and financial data provided by USAID's West Bank and Gaza mission in Tel Aviv, Israel. GAO also reviewed USAID's policies and procedures for cash transfers to the PA and its creditors and interviewed USAID, State, and PA officials about ESF assistance.
Recommendations
GAO is not making recommendations in this report.
