Defense Energy: Observations on DOD's Investments in Alternative Fuels
Highlights
What GAO Found
The Department of Defense (DOD) has purchased small quantities of alternative fuels—jet and naval distillate (known as F-76, to power ships)—for testing and demonstration purposes, but has not done so yet for military operations. DOD's testing process validates the ability of alternative fuels to meet safety, performance, and reliability standards for military equipment and platforms. From fiscal years 2007 through 2014, DOD purchased about 2.0 million gallons of alternative fuel for testing purposes, at a cost of about $58.6 million. Over the same period, it purchased about 32.0 billion gallons of petroleum fuel at a cost of about $107.2 billion. DOD has approved alternative fuels made from two production processes for use in certain items and is continuing to test others.
DOD Alternative and Conventional Fuel Purchases from Fiscal Years 2007 through 2014
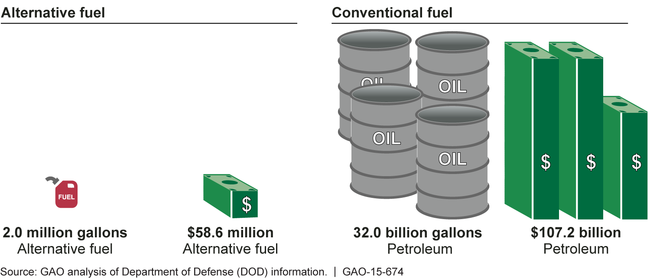
Note: The alternative fuel amounts include: Jet Propellant-8, Jet Propellant-5, and Naval Distillate. The alternative fuel cost is only the cost of fuel. The conventional fuel amounts include: Jet Propellant-8, Jet Propellant-5, Jet A, Jet A-1, and Naval Distillate. The conventional fuel cost reflects both fuel and non-product costs. All costs have been adjusted for inflation to fiscal year 2015 dollars.
DOD is currently required by law to ensure alternative fuel purchases for operational purposes are cost-competitive with conventional fuels and has a standard process to purchase large-scale volumes of all fuels. Proposals are evaluated according to technical acceptability and price. To help the Navy purchase alternative jet and naval distillate fuels blended with conventional fuels, the Department of Agriculture plans to provide funding directly to alternative fuel vendors that meet certain requirements and receive awards from DOD. These funds are intended to defray some of the alternative fuel producer's extra costs—such as costs of domestic feedstocks. Per DOD, no alternative fuel vendors have received awards so none of these funds have been paid out yet.
DOD has used financial incentives provided for by Title III of the Defense Production Act (DPA) to help facilitate the development of commercially viable plants for producing biofuels for the military and commercial sectors. To date, DOD has used this authority for two ongoing projects: Bio-Synthetic Paraffinic Kerosene and Advanced Drop-In Biofuels Production Project and the federal government's cost share for these projects was about $234.1 million.
Why GAO Did This Study
DOD is the single largest consumer of energy in the federal government, spending billions of dollars annually on petroleum fuels to support military operations. One of DOD's strategic operational energy goals is to expand its energy supply options. Investing in alternative fuels—liquid fuels, derived from non-petroleum feedstocks, whose use does not necessitate any modifications to platforms and equipment—represents one means of potentially achieving this goal.
GAO was asked to examine aspects of DOD's investment in alternative fuels. GAO reviewed the extent to which DOD (1) has purchased alternative fuels, and has demonstrated these fuels can meet its safety, performance, and reliability standards; (2) has a process for purchasing alternative fuels for military operations that takes into consideration any cost differences between alternative and conventional fuels; and (3) has used the DPA authorities to promote the development of a domestic biofuel industry.
GAO reviewed past alternative and conventional petroleum fuel procurements, as well as statutes, regulations, and DOD guidance related to fuel purchases. Also, GAO reviewed various documents on biofuel projects initiated under the DPA authority and interviewed cognizant DOD officials involved with purchasing and using fuel and administering the biofuel projects.
GAO is not making recommendations in this report. DOD provided technical comments on the findings, which GAO has incorporated where appropriate.
For more information, contact Zina Merritt at (202) 512-5257 or merrittz@gao.gov.
