Broadband: Additional Stakeholder Input Could Inform FCC Actions to Promote Competition
Highlights
What GAO Found
Selected experts and stakeholders told GAO that infrastructure costs and other factors can limit broadband deployment and the extent of broadband competition. Factors these individuals identified included providers' costs to deploy antennas, install wires or cables, and obtain permits to access existing infrastructure. Such infrastructure includes utility poles needed for deploying wired components of broadband networks. These costs can limit competition, particularly in non-urban and less populated areas, where providers' return on investment can be lower due to fewer potential customers. Experts and stakeholders also identified industry consolidation and increasing similarity of fixed and mobile broadband as factors that are likely to affect broadband competition moving forward.
Fixed Broadband Providers Reporting Download Speeds of at Least 25 Megabits per Second, as of December 2015, by Percentage of U.S. Population, as of 2010
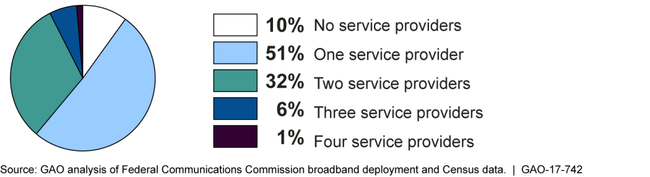
Note: Analysis combines FCC broadband deployment data from providers reporting at least 25 megabits per second download speeds and 3 megabits per second upload speeds, as of December 2015, with population data from the 2010 U.S. Decennial Census, which is the most recent nation-wide population count available.
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has undertaken rulemakings, spectrum auctions, and merger reviews to help promote competition, but lacks information on how well these actions promote competition. Despite such actions, about half of Americans have access to only one fixed provider (see figure). FCC has a process for seeking stakeholders' and others' input on broadband-related topics and annually reporting on these views, but does not solicit such input on its actions to promote competition. Such input could help FCC determine if any changes are needed to its actions to support competition relative to current and emerging factors in the broadband market. Further, FCC's annual reports contain some information on consumers' experience with broadband competition, such as the number of provider options. However, these reports do not include stakeholder input on how the number of provider options affects prices and service. Some stakeholders said that competition was important to securing lower prices and better service, while others said competition does not necessarily lead to these benefits because some providers offer the same pricing and service quality everywhere regardless of whether they face competition in a particular location. Regularly seeking stakeholder input on how varying levels of broadband deployment affect price and service quality, could help FCC to better focus its efforts to secure lower prices and higher service quality service for consumers.
Why GAO Did This Study
FCC has a role in promoting competition in the market for broadband, which provides consumers with high-speed Internet through fixed service at home and mobile service through devices such as smartphones. FCC data indicate that about 90 percent of Americans had access to fixed service as of December 2015, but that less than half had more than one choice for such service. As of that time, FCC reported that multiple providers offered mobile broadband coverage to most Americans. Mobile service increasingly allows access to Internet content that was previously accessed primarily through fixed service.
GAO was asked to examine factors affecting broadband competition. This report covers (1) selected experts' and stakeholders' views on factors affecting broadband competition and (2) how FCC promotes broadband competition and examines consumers' experience with it. GAO analyzed FCC data as of December 2015; reviewed relevant statutes and FCC documentation; interviewed FCC officials and 23 stakeholders selected to include various types of broadband providers and associations representing industry and consumers; and convened a meeting of 19 experts from academia, industry, and consumer groups with assistance from the National Academy of Sciences.
Recommendations
FCC should annually solicit and report on stakeholder input regarding (1) its actions to promote broadband competition and (2) how varying levels of broadband deployment affect prices and service quality. FCC concurred with GAO's recommendations.
Recommendations for Executive Action
| Agency Affected | Recommendation | Status Sort descending |
|---|---|---|
| Federal Communications Commission | As part of its annual reporting on the broadband market, FCC should solicit and report on the views of stakeholders and others on how well FCC's actions promote broadband competition. (Recommendation 1) |
Closed – Implemented
Broadband provides high-speed Internet service that can improve communication and drive economic growth. The Federal Communications Commission (FCC), which regulates interstate and international communications, has a role in promoting competition in the broadband market. In 2017, GAO reported that FCC had undertaken rulemakings, spectrum auctions, and other actions to help promote competition, but had not obtained information on how well its actions had promoted competition. FCC has a process for seeking stakeholders' and others' input on broadband-related topics and annually reporting on these views. However, FCC identified data limitations and other challenges to evaluating the effect of its actions on competition in the broadband market. GAO acknowledged these challenges, but noted that FCC had other ways to obtain information that could help it determine if any changes are needed in its approach for promoting competition. Federal standards for internal control, which provide a framework for identifying and addressing major performance and management challenges facing agencies, stress the importance of obtaining information from external sources that may have a significant effect on an agency achieving its goals. Without input from stakeholders and others affected by these actions, FCC may be missing key information to help it determine if any changes are needed in its approach for promoting competition. Therefore, GAO recommended that FCC solicit and report on the views of stakeholders and others on how well its actions promote broadband competition. In 2019, GAO confirmed that FCC took sufficient action to address the intent of this recommendation. Specifically, in a July 2018 solicitation for public comments related to competition in the broadband market, FCC sought feedback on how well the agency's actions promote broadband competition. In December 2018, FCC reported comments it had received from this solicitation in the first version of a biennial report on the broadband market. With these comments, FCC has information that will help the agency evaluate the effectiveness of its actions to promote competition in the market for broadband.
|
| Federal Communications Commission | As part of its annual reporting on the broadband market, FCC should solicit and report on the views of stakeholders and others on how varying levels of broadband deployment affect broadband prices and service quality. (Recommendation 2) |
Closed – Implemented
Broadband provides high-speed Internet service that can improve communication and drive economic growth. The Federal Communications Commission (FCC), which regulates interstate and international communications, has a role in promoting competition in the broadband market to help secure lower prices and higher service quality for consumers. In 2017, GAO reported that FCC has reported that competition can help consumers get lower prices and higher service quality from their broadband providers; however, the agency has not identified an approach to examine how competition affects broadband prices and service quality. FCC officials told GAO that it is difficult to assess the effect of competition on price and service quality without data showing prices and service quality indicators by the number of providers in a given area. FCC noted that it had previously sought to obtain such data, but identified various challenges to doing so, including variable pricing structures among broadband providers. Federal standards for internal control stress the importance of obtaining information from external sources that may have a significant impact on an agency achieving its goals. GAO acknowledged that additional data collection may not be a viable approach, but noted that FCC has alternative methods of information collection that could help it examine the effects of competition on price and service quality. For example, FCC seeks comments from stakeholders and others on a number of topics to inform its annual broadband progress reports. Such information could inform FCC's actions to promote competition in an effort to secure lower prices and higher quality broadband services for consumers. Therefore, GAO recommended that FCC solicit and report on the views of stakeholders and others on how varying levels of broadband deployment affect broadband prices and service quality. In 2019, GAO confirmed that FCC took sufficient action to address the intent of this recommendation. Specifically, in a July 2018 solicitation for public comments, FCC sought feedback on how varying levels of broadband deployment affect prices and service quality. In December 2018, FCC reported comments it had received from this solicitation in the first version of a biennial report on the broadband market. In May 2019, FCC also reported stakeholder comments related to agency's broadband deployment data, including service quality data. With these comments, FCC and other decision makers have information to help better prioritize and focus FCC's various efforts to promote broadband competition to secure lower prices and higher quality service for consumers in a rapidly evolving market.
|
