Elder Abuse: Federal Requirements for Oversight in Nursing Homes and Assisted Living Facilities Differ
Fast Facts
Under Medicaid and Medicare, states and the federal government share responsibility for protecting about 1.5 million nursing home and assisted living residents from elder abuse.
We compared federal requirements for reporting and investigating elder abuse in nursing homes and assisted living facilities. We found that, while the federal government sets specific requirements for nursing homes, it requires states to establish their own requirements for reporting and investigating elder abuse in assisted living facilities.

Two hands clasped together resting on a wooden table
Highlights
What GAO Found
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) oversees the Medicare and Medicaid programs and is responsible for safeguarding the health and welfare of beneficiaries living in nursing homes and assisted living facilities. This includes safeguarding older residents from abuse—referred to as elder abuse. CMS delegates responsibility for overseeing this issue to state survey agencies, which are responsible for overseeing nursing homes. When assisted living facilities provide services to Medicaid beneficiaries, they are indirectly subject to CMS oversight through the agency's oversight of state Medicaid agencies.
GAO found that there are specific federal requirements for nursing homes and state survey agencies for reporting, investigating, and notifying law enforcement about elder abuse in nursing homes. (See table below). For example, state survey agencies must prioritize reports of elder abuse in nursing homes based on CMS's specified criteria and investigate within specific time frames. In contrast, there are no similar federal requirements for assisted living facilities—which are licensed and regulated by states. Instead, CMS requires state Medicaid agencies to develop policies to ensure the reporting and investigation of elder abuse in assisted living facilities. For example, CMS requires that state Medicaid agencies establish their own policies and standards for prioritizing reports when investigating incidents in assisted living facilities. Officials from the three selected states in GAO's review said they apply certain federal nursing home requirements and investigation time frames for assisted living facilities when overseeing elder abuse.
Federal Requirements for Facilities and State Agencies to Conduct Elder Abuse Incident Reporting, Investigation, and Law Enforcement Notification
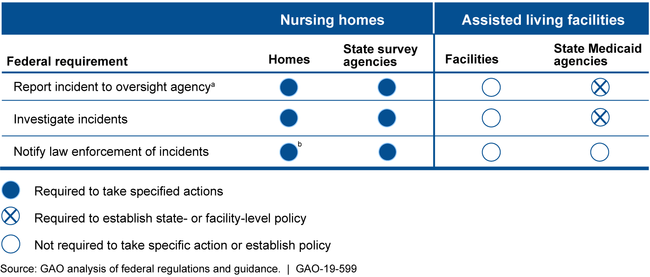
Note: This table reflects federal requirements applicable to services provided in assisted living facilities under section 1915(c) of the Social Security Act.
aNursing homes are required to ensure that incidents are reported to state survey agencies. State survey agencies are required to report certain incidents to CMS and state Medicaid agencies are required to report incidents to CMS according to the state's individual 1915(c) waiver agreement.
bFederal law requires certain covered individuals at the nursing homes to immediately report to law enforcement in addition to the state survey agency if there is a reasonable suspicion that a crime has occurred. See 42 U.S.C. § 1320b-25(b).
Why GAO Did This Study
The federal government and states share responsibility for the health and welfare of about 1.5 million individuals—most of them vulnerable older adults—receiving long-term care in nursing homes and assisted living facilities covered by Medicare and Medicaid. For nursing homes, which provide skilled nursing care, federal law defines applicable quality standards and CMS provides guidance for nursing homes and the state survey agencies to help protect residents from elder abuse. For assisted living facilities, which provide assistance with activities of daily living in a residential setting, CMS defines the framework states must establish to oversee these facilities if covered under Medicaid. This includes requiring states to demonstrate to CMS that they are assuring quality including the obligation to protect against elder abuse.
GAO was asked to review federal oversight of elder abuse reporting, investigation, and law enforcement notification in both nursing homes and assisted living facilities. In this report, GAO describes federal requirements for reporting, investigating, and notifying law enforcement about elder abuse in both types of facilities. GAO reviewed relevant laws and regulations and agency guidance, and interviewed CMS and state officials from three states selected for variation in HCBS waiver program size and geography. GAO also interviewed representatives from national stakeholder groups representing consumers, facilities, Medicaid directors, and abuse investigators. In comments on this report, HHS highlighted the distinct oversight frameworks for the two settings and noted that CMS is undertaking efforts to strengthen oversight.
For more information, contact John Dicken at (202) 512-7114 or dickenj@gao.gov.
