Nuclear Regulatory Commission: Additional Action Needed to Improve Process for Billing Licensees
Fast Facts
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission inspects and licenses nuclear power plants and other civilian uses of radioactive material. It charges licensees to recover the cost of these efforts. In fiscal 2016, for example, it collected about $321 million in related fees.
We reviewed NRC's billing process and found it is taking steps to address problems that earlier audits and some licensees identified, such as a paper billing process that did not allow sufficient review time.
We recommended, among other things, that NRC follow best practices to establish electronic billing and more fully communicate to licensees what billing information is available.

A nuclear power plant with cooling towers and related facilities.
Highlights
What GAO Found
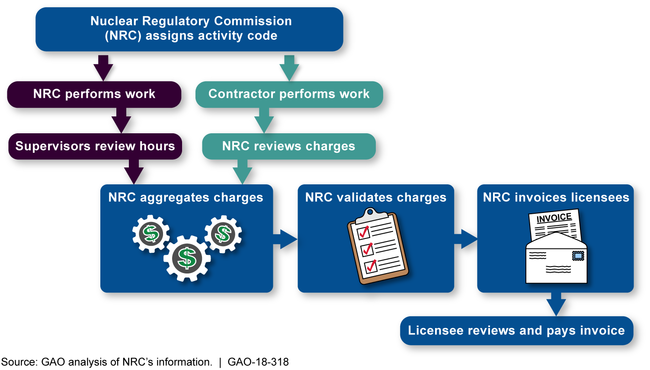
The Office of the Inspector General for the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) and internal reviews conducted by NRC identified several problems with the agency's billing process, and NRC has implemented or plans to implement several changes to address the recommendations. For example, the codes that NRC staff use to record their work hours on time cards—referred to as activity codes—did not describe the work and did not have a consistent naming convention, which increased the risk of staff charging their time to the wrong activity codes. This could lead, in some cases, to billing errors. To address these problems, NRC created a standard naming convention for activity codes that provides more information about the activity. See the figure below for the steps in NRC's billing process for work that NRC or contractor staff performed.
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission's Billing Process
Some of the 13 licensees that GAO interviewed identified challenges with NRC's billing process, including its method for delivering paper invoices by mail. For example, two of these licensees stated that with invoices taking up to 10 days to arrive in the mail, they sometimes do not have sufficient time to properly review charges and remit payment to NRC within the 30-day deadline for paying the invoice. One licensee said that delays in receiving an invoice resulted in late fees. NRC is undertaking an initiative to transition to electronic billing, which may address the challenges the licensees identified and, according to NRC staff, improve the agency's billing process. However, NRC has not developed planning documents for this initiative and, according to staff, the planning phase is already past its original deadline of October 2017. The Project Management Institute has identified standards related to project management processes, including project planning. By developing a project management plan that is consistent with best practices and includes steps for involving licensees in system development and assessing results of the project, NRC would have reasonable assurance that it can better manage its electronic billing initiative.
Why GAO Did This Study
NRC is responsible for regulating the commercial nuclear industry, including nuclear power plants. NRC provides services, such as inspections, for regulated entities that hold licenses—that is, licensees. NRC recovers the costs for these services by assessing fees and billing licensees quarterly. In fiscal year 2016, NRC collected about $321 million in service fees. From 2006 to 2016, audits of NRC's fees identified problems with NRC's billing process. For example, a 2012 audit identified about $24 million in unbilled fees from fiscal years 2011 and 2012.
GAO was asked to review NRC's billing process for service fees. This report examines (1) the actions NRC is taking to address problems with its billing process identified by internal reviews and (2) the challenges selected licensees identified with NRC's billing process and the extent to which NRC's actions are addressing them.
GAO reviewed audits of NRC's billing process and other documents related to this process. GAO also interviewed NRC staff and a nongeneralizable sample of 13 licensees, selected based on the amount of service fees charged from October 2015 through July 2017, and compared NRC's actions against criteria on internal controls and project planning.
Recommendations
GAO is making five recommendations, including that NRC develop a project management plan for its electronic billing initiative that follows project management standards and includes steps for involving licensees and assessing results. NRC agreed with these recommendations.
Recommendations for Executive Action
| Agency Affected | Recommendation | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Nuclear Regulatory Commission | The Chief Financial Officer of NRC should formally communicate to all licensees that supplemental billing information--including biweekly reports and monthly status reports on contractor charges--is available and how to request it. Formal communication that would reach all licensees could include adding information to their quarterly invoices. (Recommendation 1) |
Closed – Implemented
In 2019, NRC developed a form for licensees to request additional information on contractor charges on their bill and notified licensees that they may request additional information on contractor charges by submitting this form to NRC. In May 2020, NRC informed licensees and applicants that are enrolled in NRC's electronic billing system, called eBilling, that new reports were available that contain NRC staff hour and contractor costs that had accumulated for billing but not yet been billed. According to NRC, these new reports, called Part 170 Accruals, will be updated about every two weeks and contain all costs that have accumulated during the current billing cycle. The reports may be used to assist with estimating total invoice amounts during the billing cycle. The Part 170 Accruals are automatically provided to all licensees that are enrolled in eBilling.
|
| Nuclear Regulatory Commission | The Chief Financial Officer of NRC should develop agency policy and guidance for staff on what billing information related to contractor charges NRC staff can provide to licensees and how it should be provided. (Recommendation 2) |
Closed – Implemented
NRC developed policy and guidance related to providing contractor fees to licensees when licensees request the information. Specifically, in January 2019, NRC issued a policy memo to all NRC employees describing the agency's policy on providing contractor charges to licensees. NRC also developed associated guidance for staff on what information related to contractor charges may be provided to licensees. According to NRC documents, licensees may request the information on contractor charges using a form that NRC created in January 2019 for this purpose.
|
| Nuclear Regulatory Commission | As NRC plans its transition to electronic billing, the Chief Financial Officer of NRC should develop a project plan that incorporates standards for project management, which includes establishing plans for schedule and cost. (Recommendation 3) |
Closed – Implemented
NRC appointed a senior project manager to the electronic billing initiative and, in December 2018, completed an electronic billing project management plan that incorporated relevant standards for project management. NRC developed a comprehensive baseline project schedule with tasks, deliverables, and milestones and tracked its progress in meeting the projected schedule. NRC also tracked, on a monthly basis, its costs incurred against the contractor's estimated costs at the onset of the electronic billing initiative.
|
| Nuclear Regulatory Commission | In developing the project plan for electronic billing, the Chief Financial Officer of NRC should include steps to involve licensees in developing system capabilities, which includes soliciting and considering licensees' information needs. (Recommendation 4) |
Closed – Implemented
NRC solicited input from licensees as it developed the electronic billing system. Specifically, NRC conducted outreach to a sample of licensees to develop the system's initial concept and capabilities. In November 2018, NRC sampled another group of licensees to provide feedback on the system's aesthetics and functionality.
|
| Nuclear Regulatory Commission | In developing the project plan for electronic billing, the Chief Financial Officer of NRC should include steps to assess the results of implementing electronic billing, which includes comparing the actual performance to intended outcomes. (Recommendation 5) |
Closed – Implemented
In its March 2019 eBilling Project Management Plan, NRC defined three project metrics to assess the performance of implementing the eBilling application. The three metrics were timeliness of the invoice, rate of participation by licensees, and accuracy of invoices. In March 2021, NRC provided information on the eBilling application's performance in meeting these three metrics.
|
